Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the practice of offering shared computational resources to end-users through remote servers. It offers storage, management, and processing of data to an end-user from a centralized location, without needing powerful individual machines to carry out computational tasks.[1] The processed data files can then be transferred over network connections as documents, emails, or applications. Access and delivery of data is done through applications such as web browsers[2], which require far lower computational resources than data processing. This method is more cost-effective than the alternative.[3]
Contents
Overview
Cloud computing delivers computational capability from a centralized source to an end-user via an internet connection. Once the connection from host to end-user is made through the connection, multiple levels of service can be achieved based on the user’s needs and the system’s specifications.
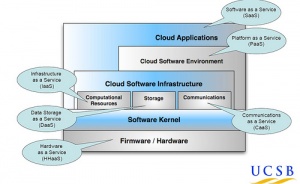
Layers of Cloud Computing
Shared cloud computing resources range from simple applications, in which users only have access to the functions provided by the application, all the way to shared operating systems which are run remotely on the server. The levels of software abstraction available to the user through the cloud are relative to the purpose of the system.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
The National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST, identifies 5 major characteristics that they believe are essential.[4]
- Customer-initiated service that provides server time and network storage.
- Network access from different electronic devices (laptops, mobile phones).
- Computer resources to be used for all different types of resources according to costumer demand.
- Capabilities for very easy revisions and access.
- Measured services that can be controlled and monitored by both the provider and customer so information will be stored accurately.
“Software as a Service”
Cloud computing often employs “Software as a Service” (SaaS)[5], in which software is “delivered” to end-users by way of network connections as opposed to being sold to the end user and operated locally. Contrasted with software being seen as a static part of the computational process, this shift in paradigm allows software’s computational nature to be seen as a resource.
"Platform as a Service"
A more server-heavy implementation of cloud computing is "Platform as a Service," or PaaS. PaaS remotely hosts software that is used to develop other software, such as Adobe Creative Suite or Microsoft Visual Studio. Paas allows multiple developers to work on the same project more easily, as well as saving the developer money and resources by liccensing and running the software remotely.
"Infrastructure as a Service"
This form of cloud computing offers the user storage, networking and processing power with few or no bundled applications. This is primarily useful for companies with large amounts of data processing to do that do not wish to maintain their own servers.
Ethical Implications
One of the largest ethical concerns deals with the illegal exchange and sharing of information within the cloud interface. This issue is hotly debated and difficult to resolve due to various copyright and licensing regulations. Cloud computing presents users with ethical dilemmas about whether or not it is legal to gain access to certain materials through a cloud sharing interface. The monitoring of these central networks keep control of who has access and to what specific pieces of information can be obtained.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Efficiency & Cost Management
Cloud computing allows efficient use of IT resources. With all computation being done in a single locale, the cloud system can be engineered to fit the demand for resources. Resources over and above demand can be powered off, or utilized in other ways to make the cloud computing system more efficient.[6]
Ease of Maintenance
With all software and hardware being stored in a single location, upgrading and updating of infrastructure must be done only one time at the central location, as opposed to multiple times at each access point. Centralized control for maintenance allows for more uniformed upgrading as well.[7]
Redundancy
The more cost-effective nature of centralized cloud resources allows system fail-safes to be put in place more easily. For instance, if one server fails, a secondary server can be used to take its place. In comparison, a set of dispersed individual computers that fail simultaneously are much more difficult to repair.[8]
System Access
When companies hire new employees they must install various software packages onto their computers. This usually is a long and tiresome process because many of these packages require certain product licensing numbers. However with cloud computing they can establish an internal network where they can access these required programs with ease because they are stored online in the cloud network. This is quicker and easier than manually downloading them onto each specific computer.
Convenience
These services have revolutionized and upgraded the utility and attractiveness of cloud computing for the average consumer. By offering a safe place to back-up files and storage, it allows consumers and companies to increase storage and capability without investing capital into new servers, infrastructure, information technology services, and licensing. Cloud computing eliminates the costly overhead for subscription servers and pay-per-use services, extending information technology's reach across the internet. Cloud services provide these ample, but innovative conveniences for users.
Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
Data Sharing & Copyright Infringement
Access to copyrighted material through the cloud raises complex legal concerns. The easy dispersion of digital material not owned by users of the cloud, but disseminated through its infrastructure can constitute copyright infringement for the user and bring legal ramifications for the cloud provider. Concerns also exist about the ownership of data stored on cloud servers. For instance, is information that is saved on the cloud the property of the individual that generated it, or property of the individual upon whose server the information is stored? [9]
Security Concerns
Information stored in a single location can potentially be subject to easier breaches in security. Having all data exist centrally allows more users to access said information, while creating a one-stop-shop for hackers to obtain classified or potentially damaging data. Ethical concerns also exist because a level of trust is required when an individual's personal information is saved on physical hardware which they cannot access or protect.[10]
Examples of Cloud Computing Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon provides various cloud services, including the S3 (Simple Storage Service) that provides data storage and EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) that is a platform to run programs and computations.
Amazon has become the industry leader in the emerging market of cloud computing. Many emerging companies, particularly those with websites that have heavy traffic or deal with fast increases in production, have turned to AWS to handle their data storage. AWS has become the de facto cloud computing platform for many because of their reputation of dependability and security, as well as an easy to use interface.
The massive growth of AMS and Amazon has prompted ZDNet's Larry Dignan to state, "Amazon will be like a book store that sells cocaine out the back door. Books will be just a front to sell storage and cloud computing."
Apple's iCloud
iCloud was released on June 6, 2011 at the Apple Worldwide Developers Conference. The free service allows users to store their mail, contacts, photos, calendar, and more information on Apple's cloud servers, and push the data to all iOS devices. This allows users' iPhones, iPads, and iMacs to be synced wirelessly and automatically. Developing from Apple's MobileMe software, iCloud is a huge improvement and makes Apple consumers' lives a lot easier.
Apple does not directly provide all of their iCloud storage. Part of the cloud services Apple utilizes is based in the Amazon Web Services cloud servers.
Dropbox
Dropbox is an application that can be installed on both your computer and your Android and iOS devices. It allows you to easily upload, access, and share files on the go. You can save something on your computer and access it on your mobile device. You can also authorize people to have access to certain Dropbox folders to facilitate easy file-sharing among multiple people.
Box.com
Box.com is a provider of cloud storage and seeks to differentiate itself among its competitors by targeting businesses and corporations. As part of the upcoming University of Michigan NextGen plan, the University of Michigan will utilize Box.com services for many of its backup data storage.
Steam Cloud
Steam cloud is part of the steam gaming platform.[11] The service allows games that run on the steam gaming platform to write and retrieve files for each user. It is can be used for settings such as keyboard, mouse and gamepad configurations, or even saved games. It is designed to make playing Steam games from different computers easier for the consumer.
See Also
References
- ↑ Cloud Computing
- ↑ Advanced Browsers Are Key To Mobile Cloud Computing
- ↑ In Cloud Computing We Trust—But Should We?
- ↑ The Real Realities of Cloud Computing: Ethical Issues for Lawyers, Law Firms, and Judges
- ↑ Cloud Computing: The Evolution of Software-as-a-Service
- ↑ The Six Benefits of Cloud Computing
- ↑ The Six Benefits of Cloud Computing
- ↑ The Six Benefits of Cloud Computing
- ↑ Cloud Computing, Digital Lockers and Copyright: The Cloudification of Entertainment
- ↑ The Privacy Implications of Cloud Computing
- ↑ http://steampowered.com/steamworks/ov_cloud.php