Difference between revisions of "Airbnb"
(→Consequences of the Sharing Economy: Moved some stuff around, formatted citation, attempted to make this section clearer) |
m (Protected "Airbnb" ([Edit=Allow only administrators] (indefinite) [Move=Allow only administrators] (indefinite))) |
||
| (94 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Nav-Bar|Topics##}}<br> | |
| − | + | {{SoftwareInfoBox | |
| + | |NAME=''Airbnb'' | ||
| + | |HEIGHT=450 | ||
| + | |TYPE=Online Hospitality Service | ||
| + | |LOGO=AirbnbLogo.png | ||
| + | |SCREENIMAGE=airbnb.jpg | ||
| + | |CAPTION="Airbnb Service" | ||
| + | |IMAGEURL=https://www.airbnb.com | ||
| + | |PRODUCT=Service | ||
| + | |LAUNCH=2008 | ||
| + | |STATUS=Active | ||
| + | |PLATFORM=Online | ||
| + | |HEADQUARTERS=San Francisco, California | ||
| + | |SITEURL=https://www.airbnb.com | ||
| + | |URLTEXT= Airbnb Official Website | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | '''Airbnb''' is a global homestay network founded in 2008 that allows people to market their residences online and seek short term tenants including vacation rentals, apartment rentals, and homestays. The platform enables their customers to experience an authentic accommodation in over 3,000,000 million residences in over 65,000 cities and 191 countries. Based in San Francisco, California, Airbnb's mission is to provide a secure marketplace for people to list, discover, and book unique travel experiences at any price point in locations all over the world. Airbnb has grown steadily and has attracted many customers away from traditional hotels. However, as the company continues to expand, there are a variety of ethical concerns that users have expressed over the company's business model. These issues include negative effects on city housing markets, racial discrimination against potential guests, and individuals posting false listings on the site, in an attempt to lure customers into booking fictional properties. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ==About Airbnb== |
| − | Chesky and Gabbia | + | ===Early History=== |
| + | Founded by college roommates Brian Chesky and Joe Gabbia in October 2007, Airbnb was initially conceptualized at the Industrial Design Conference. The pair imagined a service which provided last-minute accommodations and breakfast to travelers unable to secure a hotel booking. In early 2008, Chesky and Gabbia were joined by Nathan Blecharczyk as Chief Technical Officer and began operations as AirBed & Breakfast. They started by launching a website under the domain Airbedandbreakfast.com that offered short-term living options that included breakfast and a unique business networking opportunity for its users. Chesky and Gabbia focused initially on targeting locations hosting high-attendance events to ensure there would be travelers looking for last-minute accommodations. In order to fund the venture, the founders leveraged the 2008 U.S. Presidential Election to sell cereals, Obama O's and Cap'n McCains, to raise $30,000 of initial capital.<ref name="history">Crook, J. & Escher, A. ''A Brief History of Airbnb''. Retrieved 6 April 2017, from https://techcrunch.com/gallery/a-brief-history-of-airbnb/</ref> In 2009, Airbnb's initial office was the founders' home in San Francisco until they were able to pitch their website and idea to investors, eventually raising $20,000 from Y Combinator and $600,000 of seed funding from Sequoia Capital to rent an office and expand operations.<ref>Carson, B. (2016). How 3 guys turned renting an air mattress in their apartment into a $25 billion company. ''Business Insider.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://www.businessinsider.com/how-airbnb-was-founded-a-visual-history-2016-2/#by-summer-2008-the-founders-had-finished-a-final-version-of-air-bed-and-breakfast-and-went-to-meet-investors-the-whole-experience-had-been-redesigned-around-taking-only-three-clicks-to-book-a-stay-otherwise-it-was-too-hard-investors-werent-convinced-introductions-to-15-angel-investors-left-them-with-eight-rejections-and-seven-people-ignoring-them-entirely-7</ref> | ||
===Company expansion/Locations=== | ===Company expansion/Locations=== | ||
| − | Airbnb is established in over | + | In March 2009, AirBed & Breakfast was shortened to Airbnb as the company continued to evolve, offering unique listings including boats, planes, teepees, igloos, and tree houses.<ref>Lang, Adam. Why is it Called Airbnb? |
| + | (2014) http://www.rewindandcapture.com/why-is-it-called-airbnb/</ref> By late 2010, Airbnb raised a Series A round of $7.2 million in financing from Sequoia Capital and Greylock Partners. The company reported 700,000 nights booked, 80% of which were in the past 6 months as of November 2010. Airbnb is established in over 191 countries and over 65,000 cities.<ref name= About >About Us - Airbnb. (2017). ''Airbnb.com.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.airbnb.com/about/about-us</ref> To cater to growing demand and locations, Airbnb has offices all over the globe to maintain good customer service relationships. Currently, Airbnb has 19 offices spread across Amsterdam, Barcelona, Berlin, Beijing, Copenhagen, Dublin, London, Miami, Milan, Moscow, New Delhi, Paris, Portland, San Francisco, Sao Paulo, Seoul, Singapore, Sydney, Tokyo and Toronto.<ref>Locations | Careers at Airbnb. (2017). ''Airbnb.com.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.airbnb.com/careers/locations</ref> | ||
===Company culture=== | ===Company culture=== | ||
| − | + | According to the founders of the company, the stronger the culture is, the less corporate process a company will need.<ref>R, H.. (2015). The Importance of Company Culture at Airbnb. ''The 6Q Blog.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://inside.6q.io/the-importance-of-company-culture-at-airbnb/</ref> Airbnb treats each challenge as a problem to be solved as a team, encouraging employees to look out for each other and for upper management to trust their employees. As said by founder Brian Chesky, "Culture is a thousand things, a thousand times. It is living the core values when you hire; when you write an email; when you are working on a project; when you are walking in the hall. We have the power, by living the values, to build the culture." | |
==Products and Services== | ==Products and Services== | ||
===Home/Apartment Rental=== | ===Home/Apartment Rental=== | ||
| − | Airbnb | + | Travelers can access Airbnb via website or mobile app to search for available accommodations. Customers enter their desired duration of stay, price range, and style of accommodation they are seeking--for example, if they are looking for just one room, an entire home, or apartment. Then a customer can look through available listings and contact the host to formally book their stay.<ref>Airbnb Business Model - Business Model Toolbox. (2017). ''Business Model Toolbox.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://bmtoolbox.net/stories/airbnb/</ref> Airbnb does not formally own any rental properties, and therefore building and maintaining quality relationships with their vendors is crucial for their success. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Reviews=== | ||
| + | Both Airbnb hosts and guests are able to write public reviews of their Airbnb experiences. These public reviews create reputations for both hosts and guests online and can serve as a reference for future Airbnb users. When guests are trying to decide which Airbnb property to rent, they are able to see the number of reviews that location has received and an overall rating out of five stars. When writing reviews, guests are asked to rate their experience based on accuracy, communication, cleanliness, location, check-in, and value and have the option to include comments. Airbnb hosts also have the opportunity to rate their guests. When hosts are trying to decide whether or not to allow a certain guest to stay in their home, they can read the reviews about that guest written from previous hosts. Receiving negative reviews can affect the number of Airbnb opportunities available to both hosts and guests, with guests less likely to stay in a poorly rated property and hosts less willing to rent their property to poorly rated guests. <ref> "How Can We Help?" [https://www.airbnb.com/help/article/13/how-do-reviews-work "How Do Reviews Work? | Airbnb Help Center."] N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Apr. 2017. </ref> | ||
===Experiences=== | ===Experiences=== | ||
| − | + | In November 2016, Airbnb started providing "experiences" which are trips offered by select hosts to enrich a travelers experience through a specific activity or immersion. The service allows hosts to create an experience such as a quick workshop or a walk through a neighborhood in their city, or longer experiences over a couple of days that give guests an in-depth view into the local culture. Hosts have to write proposals for experiences which then must be approved by an Airbnb team, and after approval, hosts are free to alter the size of the group and price for the experience. Types of experiences include social impact, art & design, food & drink, sports, history, entertainment, lifestyle, music, nature, wellness, and technology. <ref>Become an Experience Host. (2017). ''Airbnb.com.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.airbnb.com/host/experiences</ref> | |
===Revenue=== | ===Revenue=== | ||
| − | Since Airbnb does not own any physical accommodations, | + | Since Airbnb does not own any physical accommodations, revenue is generated through fees charged on bookings. On each booking, Airbnb charges a 6%-12% service fee for "guest services" and also charges the host a 3% service fee. To minimize liability issues, Airbnb introduced a $50,000 physical property guarantee, voice-and-video verification systems, and a 24-hour customer support hotline.<ref>Hempel, J. (2012). Airbnb: More than a place to crash. ''Fortune.com.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://fortune.com/2012/05/03/airbnb-more-than-a-place-to-crash/</ref> They also have built a database of 3,000 professional photographers that Airbnb hosts can utilize to have their properties professionally photographed. In 2015, Airbnb generated approximately $900 million in revenue.<ref>Kokalitcheva, K. (2015). Airbnb sees $900 million in revenue to justify $24 billion valuation. ''Fortune.com.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://fortune.com/2015/06/17/airbnb-valuation-revenue/</ref> |
| + | ==Competition/Regulation== | ||
===Competition=== | ===Competition=== | ||
| − | Airbnb developed an attractive and easy to use business model for homesharing, | + | Airbnb developed an attractive and easy to use business model for homesharing, but they are not the only ones on the market. Airbnb's main competitors - [http://homeaway.com Homeaway], [http://tripping.com Tripping.com], and [http://flipkey.com Flipkey] also serve as an online marketplace for travelers to connect with hosts renting out their space for short term and long term stay. Within the accommodation industry, Airbnb also faces competition from hotels. With convenient home sharing options such as Airbnb, hotels are losing customers to cheaper options. In 2015, a third of leisure travelers used private accommodations rather than hotels, up from 10% in 2011.<ref>Glusac, E. (2017). Hotels vs. Airbnb: Let the Battle Begin. ''The New York Times.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/24/travel/airbnb-hotels.html</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ===Regulation=== | ||
| + | When deciding to become an Airbnb host, a person must be aware of the regulations that apply to their town, city, country, and/or state. Airbnb commits to working with local officials to make sure their business lawfully benefits the community. Below are a few important regulations that may apply to hosts, depending on where they live: | ||
| + | * Business licenses: many cities require that operators of certain businesses obtain a license before business can be operated. Most applications can be submitted through the local government, provided they receive the proper forms and information<ref name = City >''What regulations apply to my city?'' Airbnb Help Center, Retrieved 9 April 2017. from: https://www.airbnb.com/help/article/961/what-regulations-apply-to-my-city</ref>. | ||
| + | * Building and housing standards: Many states and local governments have regulations pertaining to the minimum construction, design, and maintenance standards for buildings. These include, but are not limited to, rules on health and safety. For Airbnb hosts in particular, residential and non-residential use regulations may be relevant to their listings. Additionally, some cities/states may require that properties undergo regular inspection to make sure it meets minimum habitability standards <ref name=City/> | ||
| + | * Zoning rules: these days, most cities and counties set out laws to define the way a person can use their home. These particular rules can most often be found in zoning codes or city ordinances. Consulting with these regulations is critical for hosts to make sure their listing(s) is consistent with the use definitions in place <ref name=City/> | ||
| + | * Special permit: Some cities and counties require that hosts obtain a special permit in order to rent our their home. If applicable, this can be done through one's city or county government <ref name=City/> | ||
| + | * Taxes: many cities, counties, and states require that hosts collect a tax for each of their overnight stays. That tax must then be paid to their city or county. Airbnb hosts are required to pay a local tax and Value Added Tax (VAT)<ref>''How do taxes work for hosts?'' Airbnb Help Center, Retrieved 9 April 2017. from: https://www.airbnb.com/help/article/481/how-do-taxes-work-for-hosts?topic=247</ref>. Residents of countries in the European Union and China may need to asses the VAT on the services they provide. | ||
| + | * Other: Airbnb encourages hosts to look deep into the other rules and contracts in their city/county. These may include homeowner association (HOA) rules, co-op rules, timeshare ownership rules, and other rules established by tenant organizations <ref name=City/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | As of February 2017, some regulators of Airbnb are not enthusiastic about the future of the sharing economy concept that the company is based off of. There have been several recent instances where cities and regions around the world have placed heavy restrictions on Airbnb rentals. Places like Berlin and San Fransisco are just a few of these places, arguing that Airbnb's are in violation of zoning codes and other local regulations. Airbnb has responded to these actions by reaching out and attempting negotiations. They have offered to collect and share tax revenue, despite the fact that they would significantly decrease their revenue generation and earning power in doing so. Airbnb is not the only peer-to-peer service provider dealing with this sort of issue<ref>Ingram, Matthew. ''The Regulators Are Finally Coming for Airbnb and Uber'',Retrieved 9 April 2017. From: http://fortune.com/2017/02/20/airbnb-uber-tech-regulations/</ref>. | ||
==Ethical Considerations== | ==Ethical Considerations== | ||
===Privacy Issues=== | ===Privacy Issues=== | ||
| − | One | + | One concern about Airbnb is privacy both for the homeowner and the guest. For the homeowner, there are issues regarding stolen or damaged property caused by the guests. These incidents may not be common, but does happen as exemplified when Airbnb received "negative press when a few consumers went public with stories of their homes being robbed or damaged by renters found through the site."<ref>Want to Rent out That Spare Room? The Growing Popularity of 'Collaborative Consumption' - Knowledge@Wharton. (2011). ''Knowledge@Wharton.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/want-to-rent-out-that-spare-room-the-growing-popularity-of-collaborative-consumption/</ref> The premise of Airbnb's existence can be partially based on the moral good in people, allowing homeowners to trust strangers to enter their homes. However, there are people that will break that social norm, causing incidents revolving property damage and loss. While Airbnb has responded to such reports by covering loss or damage from guests up to $50,000, it ultimately depends on the fundamental good nature of their users. Thus, one issue with the sharing economy is that it frequently bypasses most security checks in place of blind faith in people's goodness. |
| − | Another incident regarding privacy, but for guests, happened when a woman alleged that the apartment she rented from was equipped with a remote-controlled spy camera. | + | Another incident regarding privacy, but for guests, happened when a woman alleged that the apartment she rented from was equipped with a remote-controlled spy camera.<ref>Cooper, D. (2015). The thing you'd worry about happening in an Airbnb happened. ''Engadget.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.engadget.com/2015/12/17/airbnb-privacy-camera-snooping/</ref> It is suspected that the camera had taken explicit pictures of the woman and her partner. Even though Airbnb takes its privacy issues very seriously, it can't stop the person in possession of the pictures from uploading them on the Internet. As a result, homeowners and guests must take their own precautions to ensure privacy because Airbnb can only ensure it up to some point. |
===Consequences of the Sharing Economy=== | ===Consequences of the Sharing Economy=== | ||
| − | The sharing economy business model, which includes companies like Airbnb, [[Uber]], and [[Lyft]], connects providers and consumers to share resources and services through online application-based platforms or business transactions. | + | From the start, the promise of the sharing economy was that through digital technology and social media, markets for certain goods and services could be made more efficient. In theory, this would benefit investors, and furthermore, society. In more recent times, this "golden" future is looking a bit tarnished to some. The sharing economy business model, which includes companies like Airbnb, [[Uber]], and [[Lyft]], connects providers and consumers to share resources and services through online application-based platforms or business transactions. Because of Airbnb's sharing economy business model, the service competes against the hotel industry, which has seen revenues fall since Airbnb's introduction to the market. Airbnb's success has resulted in increased city regulations regarding sharing economies.<ref name=sharingec>Hirschon, L., Jones, M., Levin, D., McCarthy, K., Morano, B., Simon, S., & Rainwater, B. (2015). Cities, the Sharing Economy, and What's Next. <em>National League of Cities - Center for City Solutions and Applied Research.</em> Retrieved from http://web.archive.org/web/20161108222555/http://www.nlc.org/Documents/Find%20City%20Solutions/City-Solutions-and-Applied-Research/Report%20-%20%20Cities%20the%20Sharing%20Economy%20and%20Whats%20Next%20final.pdf</ref> |
| − | One argument of the sharing economy is whether it is bringing in more opportunities and creating salaried workers, or whether the net effect of displacing the workers involved in the traditional economic model is forcing them to move to lower salary part-time jobs. <ref> https://journalistsresource.org/studies/economics/business/airbnb-lyft-uber-bike-share-sharing-economy-research-roundup </ref> | + | One argument of the sharing economy is whether it is bringing in more opportunities and creating salaried workers, or whether the net effect of displacing the workers involved in the traditional economic model is forcing them to move to lower salary part-time jobs.<ref>Penn, J. & Wihbey, J. (2016). Uber, Airbnb and consequences of the sharing economy: Research roundup. ''Journalistsresource.org.'' Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://journalistsresource.org/studies/economics/business/airbnb-lyft-uber-bike-share-sharing-economy-research-roundup</ref> |
| − | == | + | NYU business professor Arun Sundararajan came out with a book in May 2016 titled “The Sharing Economy: The End of Employment and the Rise of Crowd-Based Capitalism.” In the book, Sundararajan explores how peer-to-peer commercial exchange has begun to blur the lines between personal and professional life and how it may affect the social fabric of every day life. He believes that the term "crowd-based capitalism" is more appropriate than "sharing economy", mostly because of the noncommerical connotation of the word "sharing". All in all, he finds the key downside of the the sharing economy to be its potential to lose the social safety net, meaning insurance, stable income and employment, and other benefits that are critical to the well-being of workers <ref>Anderson, Monica and Aaron Smith. ''Q&A: The impact and evolution of the sharing economy'' Retrieved 9 April 2017. from: Pew Research Center http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/05/23/qa-the-impact-and-evolution-of-the-sharing-economy/</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Housing Crises and Professional Airbnb Investors=== | ||
| + | [[File:NewYorkData.png|right|thumb|200px Table from the New York State Attorney General’s report “Airbnb in the City”]] | ||
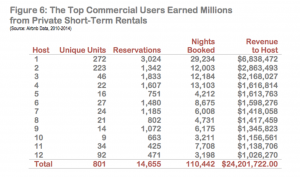
| + | Some individuals and real estate developers have begun to realize that buying city apartments for the sole use of placing them on Airbnb as rental properties can be a highly lucrative business. In 2012, Jon Wheatley bought a $40,000 dollar apartment in Las Vegas and had made a $13,000 dollar profit in a year's time by renting the property on Airbnb <ref name="realestate"> "The Rise of the Professional Airbnb Investor." Priceonomics. Priceonomics.com. Jan 19, 2017. https://priceonomics.com/will-real-estate-investors-take-over-airbnb/ </ref>. While this idea may just be straightforward economics, it becomes problematic in cities like New York and San Francisco where housing is scarce, prices are high, and wealthy investors buying up properties would serve to exacerbate the problem. In a 2014 report of Airbnb users in New York City, while 94% of users rented out 2 units or fewer, 6% of users were renting between 3 and 272 units and were responsible for over a third of all bookings and Airbnb rental income in the entire city <ref name="realestate"/>. Some people are afraid this will take Airbnb down the path of other decentralized services such as eBay, where anyone can post an auction but people who operate as full-time "power sellers" dominate the market <ref name="realestate"/>. The rise of professional Airbnb investors has led to public backlash, especially in places with high housing costs such as San Francisco in New York, as residents believe it will drive up rents and they are unhappy with the increasing amounts of strangers moving in and out of their apartment complexes on a regular basis <ref name="realestate"/>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In response, cities like San Francisco and New York have begun passing regulations to try to curtail these sorts of activities. In 2015, San Francisco passed a law that limited the number of days that apartments can be rented out annually and requires hosts to register with the city <ref name="airbnb"> "AIRBNB’S LEGAL AND ETHICAL WOES: A STORY OF DRAMATIC EXPANSION AND TIMELY REALITY CHECKS." Elegran. July 12, 2016. https://www.elegran.com/blog/2016/07/airbnbs-legal-and-ethical-woes-a-story-of-dramatic-expansion-and-timely-reality-checks </ref>. In New York, laws have been passed that prevent rentals shorter than 30 days without the presence of a permanent resident and banning hosts from renting out entire apartments <ref name="airbnb"/>. The city of Berlin, Germany has entirely banned hosts from renting out properties for short-term stays with hefty penalty fines <ref name="airbnb"/>. However, other cities are taking a different approach and heralding the rise of Airbnb in the sharing economy as a potent source of tourist revenue. London recently repealed a law that required approval to rent an apartment for less than 90 days, encouraging the growth of the Airbnb market in the city <ref name="airbnb"/>. As Airbnb continues to grow in market share, more cities will have no make a choice about whether to defend the rights of their permanent residents, prevent gentrification, and stabilize their housing markets, or reap the benefits of increased tourism and taxation on Airbnb properties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sole Proprietorship of Exchange=== | ||
| + | Like many digital and virtual market places found in the world of sharing economy corporations, Airbnb attempts to protect the integrity their platform and its revenue by regulating the interactions between its users. The website's Terms of Service and User Conduct Policy forbid the platform's users from contacting one another outside of the platform. <ref name="termsOfService">"Airbnb User Terms of Service." Airbnb.com. Airbnb, 27 Oct. 2016. Web. <https://www.airbnb.com/terms>.</ref> | ||
| + | {{Quotation|You understand and agree that you are solely responsible for compliance with any and all laws, rules, regulations, and Tax obligations that may apply to your use of the Site, Application, Services and Collective Content. In connection with your use of the Site, Application, Services and Collective Content, you may not and you agree that you will not: | ||
| + | -use the Site, Application, Services or Collective Content to find a Host or Guest and then complete a Booking of an Accommodation independent of the Site, Application or Services, in order to circumvent the obligation to pay any Service Fees related to Airbnb’s provision of the Services or for any other reasons. | ||
| + | |||
| + | -use the Site, Application, Services or Collective Content for any commercial or other purposes that are not expressly permitted by these Terms.<ref name="termsOfService"/> | ||
| + | |Airbnb Terms of Service and User Policy||skip italics to use '' '' for italics}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some would regard this attempt to restrict user behavior as dubious on Airbnb's part, given that searching for lodging accommodations and subsequently negotiating a rate is not a process unique to Airbnb. Disregarding the enforceability of Airbnb's policy, it thus seems ethically questionable that the firm would threaten to bar users who violate this policy from the platform. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Claims of Discrimination=== | ||
| + | Airbnb has faced backlash in recent years for enabling discrimination between users. The site requires travelers and hosts to have profile photos, making easier for users to discriminate against others on the basis of race. A growing number of black Airbnb travelers have reported experiencing racism while using the site and its services.<ref name="Discrimination">Glusac, E. (2016). "As Airbnb Grows, So Do Claims of Discrimination". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from https://www.nytimes.com/2016/06/26/travel/airbnb-discrimination-lawsuit.html?_r=0</ref> Some reported being mistaken for thieves upon arriving at the property they rented.<ref name="Discrimination"/> Another reported a host cancelling his booking and subsequently posting hateful language online.<ref name="Discrimination"/> One of the most infamous cases occurred in 2016 when Gregory Selden, a 25-year-old black man sued Airbnb for discrimination. Selden reported being denied by a host when requesting a booking from his personal profile but being accepted when requesting the same booking from two fake profiles of white men.<ref name="Sued">King, H. (2016). "Airbnb sued for discrimination". CNN. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from http://money.cnn.com/2016/05/18/technology/airbnb-lawsuit-discrimination/</ref> Shortly after this incident, Harvard Business School conducted a study and found that Airbnb applications from guests with stereotypically black names were 16% less likely to be accepted than identical applications from guests with stereotypically white names.<ref>Edelman, B., Luca, M., Svirsky, D. (2016). "Racial Discrimination in the Sharing Economy: Evidence from a Field Experiment". Harvard Business School. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from Racial Discrimination in the Sharing Economy: Evidence from a Field Experiment</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The case of Dyne Suh, an Asian-American woman from Southern California, was another incident of discrimination between an Airbnb host and guest. Suh had booked a cabin in Big Bear, CA for a weekend with friends a month in advance to her drive up. Suh had been in contact with the host, asking to add two additional people to the original reservation, and had received confirmation that it was okay. However, upon arrival, she was turned away from the host whose reason for denying access was, "I wouldn’t rent to (you) if (you) were the last person on earth...One word says it all. Asian", followed by a comment about supporting Trump and targeting foreigners.<ref>"Airbnb Bans Trump Supporter for Canceling Asian Guest's Reservation." Fox News. FOX News Network, 7 Apr. 2017. Web. 13 Apr. 2017. <http://www.foxnews.com/travel/2017/04/07/airbnb-bans-trump-supporter-for-canceling-asian-guest-s-reservation.htm>.</ref> Suh's case demonstrates Airbnb hosts exploiting their access to the guests' personal information, such as their profile photo which can indicate one's ethnicity, to intentionally cause harm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main difference between Airbnb and a hotel is that Airbnb hosts can see potential renters before accepting a booking.<ref name="Sued"/> However, Airbnb still qualifies as a public accommodation under the law<ref name="Sued"/>: “When it comes to accepting guests, hosts may stipulate that they don’t want smokers or teenagers renting their property, but federal law prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex or national origin,” .<ref name="Discrimination"/> In addition, Airbnb didn’t originally have policies or company training regarding nondiscrimination.<ref name="Discrimination"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | More recently, Airbnb has taken steps to reduce the prominence of discrimination on their service. Guest photos are less prominent during the booking process, and photos of hosts are no longer included on the search listings page.<ref name = "Improvements">McGee, C. (2017). "How Airbnb's redesign aims to combat discrimination on the service". CNBC. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from http://www.cnbc.com/2017/04/07/airbnb-experimenting-with-site-design-to-fight-discrimination.html</ref> The company has hired a team of engineers, data scientists, researchers, and designers specifically designated to reduce bias on the site.<ref name="Improvements"/> In addition, the “Instant Book” feature acts as a hotel booking engine, making the Airbnb booking process faster and identity-free.<ref name="Discrimination"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===False Listings and Scamming=== | ||
| + | While Airbnb has taken many steps to verify the validity of its hosts and listings, there have been some cases of hosts posting false information to lure users to book fake listings. In February 2017, an Airbnb host that joined in September 2016 created a listing of a six bedroom villa in Australia in $652 per night. <ref name = False Listings">Rahman, K (2017). "Scammers using fake Airbnb listings dupe tourists". Daily Mail Australia. Retrieved 19 April 2017, from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-4239456/Scammers-using-fake-Airbnb-listings-dupe-tourists.html</ref> A reverse Google search showed that the photo used to display the "villa" was actually taken off a property in Florida in the United States, while the address listed was a hostel in Bondi Beach. The listing was live on the site until the following Sunday, where it was taken down by Airbnb. While this is a single case that was widely reported, there could have been many other cases of false listings luring users of the platform to pay money and book false stays. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This kind of action is extremely unethical as well as illegal and Airbnb has spoken out to take serious measures in vetting new hosts and their properties. However, unless the background of every single new listing and host to the website is carefully checked, there is not a surefire way for the company to make sure this never happens. Manipulating the platform in such a way to take advantage of users is directly against the assumption of Airbnb that most of its users are morally good. This problem illustrates the flaw of a platform such as Airbnb since people are not simply offering services/goods to buy or sell but actual physical spaces which would make people assume that everyone on the platform is trustworthy since entering a property is an extreme exercise of trust from host to guest. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Landlord Permissions=== | ||
| + | While Airbnb encourages their hosts to look into local regulations and to talk to their landlords and get permission to rent out their apartments, this does not always happen. <ref>How to Get Landlord Permission to Host on Airbnb http://learnairbnb.com/airbnb-landlord-permission-negotiation/</ref>. Many hosts will just rent out their rooms and/or apartments without their landlords knowledge or permission. This can create many ethical and legal issues. Many landlords do not want Airbnb guests for very valid reasons, such as it can invalidate the insurance that they have on the property. It can also make guests feel uncomfortable when they know that they are not supposed to be staying there. There are different laws in different countries, but this could result in the guest getting kicked out of the property depending on the local laws. It could also ultimately get the host evicted from their apartment by the landlord. <ref>Host is subletting without landlord's permission https://community.withairbnb.com/t5/Travelers/Host-is-subletting-without-landlord-s-permission-will-I-the/td-p/196171</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See Also== | ||
| + | {{resource| | ||
| + | *[[Information Security]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Blue Star]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 19:47, 23 April 2017
|
Airbnb is a global homestay network founded in 2008 that allows people to market their residences online and seek short term tenants including vacation rentals, apartment rentals, and homestays. The platform enables their customers to experience an authentic accommodation in over 3,000,000 million residences in over 65,000 cities and 191 countries. Based in San Francisco, California, Airbnb's mission is to provide a secure marketplace for people to list, discover, and book unique travel experiences at any price point in locations all over the world. Airbnb has grown steadily and has attracted many customers away from traditional hotels. However, as the company continues to expand, there are a variety of ethical concerns that users have expressed over the company's business model. These issues include negative effects on city housing markets, racial discrimination against potential guests, and individuals posting false listings on the site, in an attempt to lure customers into booking fictional properties.
Contents
About Airbnb
Early History
Founded by college roommates Brian Chesky and Joe Gabbia in October 2007, Airbnb was initially conceptualized at the Industrial Design Conference. The pair imagined a service which provided last-minute accommodations and breakfast to travelers unable to secure a hotel booking. In early 2008, Chesky and Gabbia were joined by Nathan Blecharczyk as Chief Technical Officer and began operations as AirBed & Breakfast. They started by launching a website under the domain Airbedandbreakfast.com that offered short-term living options that included breakfast and a unique business networking opportunity for its users. Chesky and Gabbia focused initially on targeting locations hosting high-attendance events to ensure there would be travelers looking for last-minute accommodations. In order to fund the venture, the founders leveraged the 2008 U.S. Presidential Election to sell cereals, Obama O's and Cap'n McCains, to raise $30,000 of initial capital.[1] In 2009, Airbnb's initial office was the founders' home in San Francisco until they were able to pitch their website and idea to investors, eventually raising $20,000 from Y Combinator and $600,000 of seed funding from Sequoia Capital to rent an office and expand operations.[2]
Company expansion/Locations
In March 2009, AirBed & Breakfast was shortened to Airbnb as the company continued to evolve, offering unique listings including boats, planes, teepees, igloos, and tree houses.[3] By late 2010, Airbnb raised a Series A round of $7.2 million in financing from Sequoia Capital and Greylock Partners. The company reported 700,000 nights booked, 80% of which were in the past 6 months as of November 2010. Airbnb is established in over 191 countries and over 65,000 cities.[4] To cater to growing demand and locations, Airbnb has offices all over the globe to maintain good customer service relationships. Currently, Airbnb has 19 offices spread across Amsterdam, Barcelona, Berlin, Beijing, Copenhagen, Dublin, London, Miami, Milan, Moscow, New Delhi, Paris, Portland, San Francisco, Sao Paulo, Seoul, Singapore, Sydney, Tokyo and Toronto.[5]
Company culture
According to the founders of the company, the stronger the culture is, the less corporate process a company will need.[6] Airbnb treats each challenge as a problem to be solved as a team, encouraging employees to look out for each other and for upper management to trust their employees. As said by founder Brian Chesky, "Culture is a thousand things, a thousand times. It is living the core values when you hire; when you write an email; when you are working on a project; when you are walking in the hall. We have the power, by living the values, to build the culture."
Products and Services
Home/Apartment Rental
Travelers can access Airbnb via website or mobile app to search for available accommodations. Customers enter their desired duration of stay, price range, and style of accommodation they are seeking--for example, if they are looking for just one room, an entire home, or apartment. Then a customer can look through available listings and contact the host to formally book their stay.[7] Airbnb does not formally own any rental properties, and therefore building and maintaining quality relationships with their vendors is crucial for their success.
Reviews
Both Airbnb hosts and guests are able to write public reviews of their Airbnb experiences. These public reviews create reputations for both hosts and guests online and can serve as a reference for future Airbnb users. When guests are trying to decide which Airbnb property to rent, they are able to see the number of reviews that location has received and an overall rating out of five stars. When writing reviews, guests are asked to rate their experience based on accuracy, communication, cleanliness, location, check-in, and value and have the option to include comments. Airbnb hosts also have the opportunity to rate their guests. When hosts are trying to decide whether or not to allow a certain guest to stay in their home, they can read the reviews about that guest written from previous hosts. Receiving negative reviews can affect the number of Airbnb opportunities available to both hosts and guests, with guests less likely to stay in a poorly rated property and hosts less willing to rent their property to poorly rated guests. [8]
Experiences
In November 2016, Airbnb started providing "experiences" which are trips offered by select hosts to enrich a travelers experience through a specific activity or immersion. The service allows hosts to create an experience such as a quick workshop or a walk through a neighborhood in their city, or longer experiences over a couple of days that give guests an in-depth view into the local culture. Hosts have to write proposals for experiences which then must be approved by an Airbnb team, and after approval, hosts are free to alter the size of the group and price for the experience. Types of experiences include social impact, art & design, food & drink, sports, history, entertainment, lifestyle, music, nature, wellness, and technology. [9]
Revenue
Since Airbnb does not own any physical accommodations, revenue is generated through fees charged on bookings. On each booking, Airbnb charges a 6%-12% service fee for "guest services" and also charges the host a 3% service fee. To minimize liability issues, Airbnb introduced a $50,000 physical property guarantee, voice-and-video verification systems, and a 24-hour customer support hotline.[10] They also have built a database of 3,000 professional photographers that Airbnb hosts can utilize to have their properties professionally photographed. In 2015, Airbnb generated approximately $900 million in revenue.[11]
Competition/Regulation
Competition
Airbnb developed an attractive and easy to use business model for homesharing, but they are not the only ones on the market. Airbnb's main competitors - Homeaway, Tripping.com, and Flipkey also serve as an online marketplace for travelers to connect with hosts renting out their space for short term and long term stay. Within the accommodation industry, Airbnb also faces competition from hotels. With convenient home sharing options such as Airbnb, hotels are losing customers to cheaper options. In 2015, a third of leisure travelers used private accommodations rather than hotels, up from 10% in 2011.[12]
Regulation
When deciding to become an Airbnb host, a person must be aware of the regulations that apply to their town, city, country, and/or state. Airbnb commits to working with local officials to make sure their business lawfully benefits the community. Below are a few important regulations that may apply to hosts, depending on where they live:
- Business licenses: many cities require that operators of certain businesses obtain a license before business can be operated. Most applications can be submitted through the local government, provided they receive the proper forms and information[13].
- Building and housing standards: Many states and local governments have regulations pertaining to the minimum construction, design, and maintenance standards for buildings. These include, but are not limited to, rules on health and safety. For Airbnb hosts in particular, residential and non-residential use regulations may be relevant to their listings. Additionally, some cities/states may require that properties undergo regular inspection to make sure it meets minimum habitability standards [13]
- Zoning rules: these days, most cities and counties set out laws to define the way a person can use their home. These particular rules can most often be found in zoning codes or city ordinances. Consulting with these regulations is critical for hosts to make sure their listing(s) is consistent with the use definitions in place [13]
- Special permit: Some cities and counties require that hosts obtain a special permit in order to rent our their home. If applicable, this can be done through one's city or county government [13]
- Taxes: many cities, counties, and states require that hosts collect a tax for each of their overnight stays. That tax must then be paid to their city or county. Airbnb hosts are required to pay a local tax and Value Added Tax (VAT)[14]. Residents of countries in the European Union and China may need to asses the VAT on the services they provide.
- Other: Airbnb encourages hosts to look deep into the other rules and contracts in their city/county. These may include homeowner association (HOA) rules, co-op rules, timeshare ownership rules, and other rules established by tenant organizations [13]
As of February 2017, some regulators of Airbnb are not enthusiastic about the future of the sharing economy concept that the company is based off of. There have been several recent instances where cities and regions around the world have placed heavy restrictions on Airbnb rentals. Places like Berlin and San Fransisco are just a few of these places, arguing that Airbnb's are in violation of zoning codes and other local regulations. Airbnb has responded to these actions by reaching out and attempting negotiations. They have offered to collect and share tax revenue, despite the fact that they would significantly decrease their revenue generation and earning power in doing so. Airbnb is not the only peer-to-peer service provider dealing with this sort of issue[15].
Ethical Considerations
Privacy Issues
One concern about Airbnb is privacy both for the homeowner and the guest. For the homeowner, there are issues regarding stolen or damaged property caused by the guests. These incidents may not be common, but does happen as exemplified when Airbnb received "negative press when a few consumers went public with stories of their homes being robbed or damaged by renters found through the site."[16] The premise of Airbnb's existence can be partially based on the moral good in people, allowing homeowners to trust strangers to enter their homes. However, there are people that will break that social norm, causing incidents revolving property damage and loss. While Airbnb has responded to such reports by covering loss or damage from guests up to $50,000, it ultimately depends on the fundamental good nature of their users. Thus, one issue with the sharing economy is that it frequently bypasses most security checks in place of blind faith in people's goodness.
Another incident regarding privacy, but for guests, happened when a woman alleged that the apartment she rented from was equipped with a remote-controlled spy camera.[17] It is suspected that the camera had taken explicit pictures of the woman and her partner. Even though Airbnb takes its privacy issues very seriously, it can't stop the person in possession of the pictures from uploading them on the Internet. As a result, homeowners and guests must take their own precautions to ensure privacy because Airbnb can only ensure it up to some point.
Consequences of the Sharing Economy
From the start, the promise of the sharing economy was that through digital technology and social media, markets for certain goods and services could be made more efficient. In theory, this would benefit investors, and furthermore, society. In more recent times, this "golden" future is looking a bit tarnished to some. The sharing economy business model, which includes companies like Airbnb, Uber, and Lyft, connects providers and consumers to share resources and services through online application-based platforms or business transactions. Because of Airbnb's sharing economy business model, the service competes against the hotel industry, which has seen revenues fall since Airbnb's introduction to the market. Airbnb's success has resulted in increased city regulations regarding sharing economies.[18]
One argument of the sharing economy is whether it is bringing in more opportunities and creating salaried workers, or whether the net effect of displacing the workers involved in the traditional economic model is forcing them to move to lower salary part-time jobs.[19]
NYU business professor Arun Sundararajan came out with a book in May 2016 titled “The Sharing Economy: The End of Employment and the Rise of Crowd-Based Capitalism.” In the book, Sundararajan explores how peer-to-peer commercial exchange has begun to blur the lines between personal and professional life and how it may affect the social fabric of every day life. He believes that the term "crowd-based capitalism" is more appropriate than "sharing economy", mostly because of the noncommerical connotation of the word "sharing". All in all, he finds the key downside of the the sharing economy to be its potential to lose the social safety net, meaning insurance, stable income and employment, and other benefits that are critical to the well-being of workers [20].
Housing Crises and Professional Airbnb Investors
Some individuals and real estate developers have begun to realize that buying city apartments for the sole use of placing them on Airbnb as rental properties can be a highly lucrative business. In 2012, Jon Wheatley bought a $40,000 dollar apartment in Las Vegas and had made a $13,000 dollar profit in a year's time by renting the property on Airbnb [21]. While this idea may just be straightforward economics, it becomes problematic in cities like New York and San Francisco where housing is scarce, prices are high, and wealthy investors buying up properties would serve to exacerbate the problem. In a 2014 report of Airbnb users in New York City, while 94% of users rented out 2 units or fewer, 6% of users were renting between 3 and 272 units and were responsible for over a third of all bookings and Airbnb rental income in the entire city [21]. Some people are afraid this will take Airbnb down the path of other decentralized services such as eBay, where anyone can post an auction but people who operate as full-time "power sellers" dominate the market [21]. The rise of professional Airbnb investors has led to public backlash, especially in places with high housing costs such as San Francisco in New York, as residents believe it will drive up rents and they are unhappy with the increasing amounts of strangers moving in and out of their apartment complexes on a regular basis [21].
In response, cities like San Francisco and New York have begun passing regulations to try to curtail these sorts of activities. In 2015, San Francisco passed a law that limited the number of days that apartments can be rented out annually and requires hosts to register with the city [22]. In New York, laws have been passed that prevent rentals shorter than 30 days without the presence of a permanent resident and banning hosts from renting out entire apartments [22]. The city of Berlin, Germany has entirely banned hosts from renting out properties for short-term stays with hefty penalty fines [22]. However, other cities are taking a different approach and heralding the rise of Airbnb in the sharing economy as a potent source of tourist revenue. London recently repealed a law that required approval to rent an apartment for less than 90 days, encouraging the growth of the Airbnb market in the city [22]. As Airbnb continues to grow in market share, more cities will have no make a choice about whether to defend the rights of their permanent residents, prevent gentrification, and stabilize their housing markets, or reap the benefits of increased tourism and taxation on Airbnb properties.
Sole Proprietorship of Exchange
Like many digital and virtual market places found in the world of sharing economy corporations, Airbnb attempts to protect the integrity their platform and its revenue by regulating the interactions between its users. The website's Terms of Service and User Conduct Policy forbid the platform's users from contacting one another outside of the platform. [23]
You understand and agree that you are solely responsible for compliance with any and all laws, rules, regulations, and Tax obligations that may apply to your use of the Site, Application, Services and Collective Content. In connection with your use of the Site, Application, Services and Collective Content, you may not and you agree that you will not:-use the Site, Application, Services or Collective Content to find a Host or Guest and then complete a Booking of an Accommodation independent of the Site, Application or Services, in order to circumvent the obligation to pay any Service Fees related to Airbnb’s provision of the Services or for any other reasons.
-use the Site, Application, Services or Collective Content for any commercial or other purposes that are not expressly permitted by these Terms.[23]
Some would regard this attempt to restrict user behavior as dubious on Airbnb's part, given that searching for lodging accommodations and subsequently negotiating a rate is not a process unique to Airbnb. Disregarding the enforceability of Airbnb's policy, it thus seems ethically questionable that the firm would threaten to bar users who violate this policy from the platform.
Claims of Discrimination
Airbnb has faced backlash in recent years for enabling discrimination between users. The site requires travelers and hosts to have profile photos, making easier for users to discriminate against others on the basis of race. A growing number of black Airbnb travelers have reported experiencing racism while using the site and its services.[24] Some reported being mistaken for thieves upon arriving at the property they rented.[24] Another reported a host cancelling his booking and subsequently posting hateful language online.[24] One of the most infamous cases occurred in 2016 when Gregory Selden, a 25-year-old black man sued Airbnb for discrimination. Selden reported being denied by a host when requesting a booking from his personal profile but being accepted when requesting the same booking from two fake profiles of white men.[25] Shortly after this incident, Harvard Business School conducted a study and found that Airbnb applications from guests with stereotypically black names were 16% less likely to be accepted than identical applications from guests with stereotypically white names.[26]
The case of Dyne Suh, an Asian-American woman from Southern California, was another incident of discrimination between an Airbnb host and guest. Suh had booked a cabin in Big Bear, CA for a weekend with friends a month in advance to her drive up. Suh had been in contact with the host, asking to add two additional people to the original reservation, and had received confirmation that it was okay. However, upon arrival, she was turned away from the host whose reason for denying access was, "I wouldn’t rent to (you) if (you) were the last person on earth...One word says it all. Asian", followed by a comment about supporting Trump and targeting foreigners.[27] Suh's case demonstrates Airbnb hosts exploiting their access to the guests' personal information, such as their profile photo which can indicate one's ethnicity, to intentionally cause harm.
The main difference between Airbnb and a hotel is that Airbnb hosts can see potential renters before accepting a booking.[25] However, Airbnb still qualifies as a public accommodation under the law[25]: “When it comes to accepting guests, hosts may stipulate that they don’t want smokers or teenagers renting their property, but federal law prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex or national origin,” .[24] In addition, Airbnb didn’t originally have policies or company training regarding nondiscrimination.[24]
More recently, Airbnb has taken steps to reduce the prominence of discrimination on their service. Guest photos are less prominent during the booking process, and photos of hosts are no longer included on the search listings page.[28] The company has hired a team of engineers, data scientists, researchers, and designers specifically designated to reduce bias on the site.[28] In addition, the “Instant Book” feature acts as a hotel booking engine, making the Airbnb booking process faster and identity-free.[24]
False Listings and Scamming
While Airbnb has taken many steps to verify the validity of its hosts and listings, there have been some cases of hosts posting false information to lure users to book fake listings. In February 2017, an Airbnb host that joined in September 2016 created a listing of a six bedroom villa in Australia in $652 per night. [29] A reverse Google search showed that the photo used to display the "villa" was actually taken off a property in Florida in the United States, while the address listed was a hostel in Bondi Beach. The listing was live on the site until the following Sunday, where it was taken down by Airbnb. While this is a single case that was widely reported, there could have been many other cases of false listings luring users of the platform to pay money and book false stays.
This kind of action is extremely unethical as well as illegal and Airbnb has spoken out to take serious measures in vetting new hosts and their properties. However, unless the background of every single new listing and host to the website is carefully checked, there is not a surefire way for the company to make sure this never happens. Manipulating the platform in such a way to take advantage of users is directly against the assumption of Airbnb that most of its users are morally good. This problem illustrates the flaw of a platform such as Airbnb since people are not simply offering services/goods to buy or sell but actual physical spaces which would make people assume that everyone on the platform is trustworthy since entering a property is an extreme exercise of trust from host to guest.
Landlord Permissions
While Airbnb encourages their hosts to look into local regulations and to talk to their landlords and get permission to rent out their apartments, this does not always happen. [30]. Many hosts will just rent out their rooms and/or apartments without their landlords knowledge or permission. This can create many ethical and legal issues. Many landlords do not want Airbnb guests for very valid reasons, such as it can invalidate the insurance that they have on the property. It can also make guests feel uncomfortable when they know that they are not supposed to be staying there. There are different laws in different countries, but this could result in the guest getting kicked out of the property depending on the local laws. It could also ultimately get the host evicted from their apartment by the landlord. [31].
See Also
References
- ↑ Crook, J. & Escher, A. A Brief History of Airbnb. Retrieved 6 April 2017, from https://techcrunch.com/gallery/a-brief-history-of-airbnb/
- ↑ Carson, B. (2016). How 3 guys turned renting an air mattress in their apartment into a $25 billion company. Business Insider. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://www.businessinsider.com/how-airbnb-was-founded-a-visual-history-2016-2/#by-summer-2008-the-founders-had-finished-a-final-version-of-air-bed-and-breakfast-and-went-to-meet-investors-the-whole-experience-had-been-redesigned-around-taking-only-three-clicks-to-book-a-stay-otherwise-it-was-too-hard-investors-werent-convinced-introductions-to-15-angel-investors-left-them-with-eight-rejections-and-seven-people-ignoring-them-entirely-7
- ↑ Lang, Adam. Why is it Called Airbnb? (2014) http://www.rewindandcapture.com/why-is-it-called-airbnb/
- ↑ About Us - Airbnb. (2017). Airbnb.com. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.airbnb.com/about/about-us
- ↑ Locations | Careers at Airbnb. (2017). Airbnb.com. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.airbnb.com/careers/locations
- ↑ R, H.. (2015). The Importance of Company Culture at Airbnb. The 6Q Blog. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://inside.6q.io/the-importance-of-company-culture-at-airbnb/
- ↑ Airbnb Business Model - Business Model Toolbox. (2017). Business Model Toolbox. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://bmtoolbox.net/stories/airbnb/
- ↑ "How Can We Help?" "How Do Reviews Work? | Airbnb Help Center." N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Apr. 2017.
- ↑ Become an Experience Host. (2017). Airbnb.com. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.airbnb.com/host/experiences
- ↑ Hempel, J. (2012). Airbnb: More than a place to crash. Fortune.com. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://fortune.com/2012/05/03/airbnb-more-than-a-place-to-crash/
- ↑ Kokalitcheva, K. (2015). Airbnb sees $900 million in revenue to justify $24 billion valuation. Fortune.com. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://fortune.com/2015/06/17/airbnb-valuation-revenue/
- ↑ Glusac, E. (2017). Hotels vs. Airbnb: Let the Battle Begin. The New York Times. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/24/travel/airbnb-hotels.html
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 What regulations apply to my city? Airbnb Help Center, Retrieved 9 April 2017. from: https://www.airbnb.com/help/article/961/what-regulations-apply-to-my-city
- ↑ How do taxes work for hosts? Airbnb Help Center, Retrieved 9 April 2017. from: https://www.airbnb.com/help/article/481/how-do-taxes-work-for-hosts?topic=247
- ↑ Ingram, Matthew. The Regulators Are Finally Coming for Airbnb and Uber,Retrieved 9 April 2017. From: http://fortune.com/2017/02/20/airbnb-uber-tech-regulations/
- ↑ Want to Rent out That Spare Room? The Growing Popularity of 'Collaborative Consumption' - Knowledge@Wharton. (2011). Knowledge@Wharton. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/want-to-rent-out-that-spare-room-the-growing-popularity-of-collaborative-consumption/
- ↑ Cooper, D. (2015). The thing you'd worry about happening in an Airbnb happened. Engadget. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://www.engadget.com/2015/12/17/airbnb-privacy-camera-snooping/
- ↑ Hirschon, L., Jones, M., Levin, D., McCarthy, K., Morano, B., Simon, S., & Rainwater, B. (2015). Cities, the Sharing Economy, and What's Next. National League of Cities - Center for City Solutions and Applied Research. Retrieved from http://web.archive.org/web/20161108222555/http://www.nlc.org/Documents/Find%20City%20Solutions/City-Solutions-and-Applied-Research/Report%20-%20%20Cities%20the%20Sharing%20Economy%20and%20Whats%20Next%20final.pdf
- ↑ Penn, J. & Wihbey, J. (2016). Uber, Airbnb and consequences of the sharing economy: Research roundup. Journalistsresource.org. Retrieved 8 April 2017, from https://journalistsresource.org/studies/economics/business/airbnb-lyft-uber-bike-share-sharing-economy-research-roundup
- ↑ Anderson, Monica and Aaron Smith. Q&A: The impact and evolution of the sharing economy Retrieved 9 April 2017. from: Pew Research Center http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/05/23/qa-the-impact-and-evolution-of-the-sharing-economy/
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 "The Rise of the Professional Airbnb Investor." Priceonomics. Priceonomics.com. Jan 19, 2017. https://priceonomics.com/will-real-estate-investors-take-over-airbnb/
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 "AIRBNB’S LEGAL AND ETHICAL WOES: A STORY OF DRAMATIC EXPANSION AND TIMELY REALITY CHECKS." Elegran. July 12, 2016. https://www.elegran.com/blog/2016/07/airbnbs-legal-and-ethical-woes-a-story-of-dramatic-expansion-and-timely-reality-checks
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Airbnb User Terms of Service." Airbnb.com. Airbnb, 27 Oct. 2016. Web. <https://www.airbnb.com/terms>.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 24.4 24.5 Glusac, E. (2016). "As Airbnb Grows, So Do Claims of Discrimination". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from https://www.nytimes.com/2016/06/26/travel/airbnb-discrimination-lawsuit.html?_r=0
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 King, H. (2016). "Airbnb sued for discrimination". CNN. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from http://money.cnn.com/2016/05/18/technology/airbnb-lawsuit-discrimination/
- ↑ Edelman, B., Luca, M., Svirsky, D. (2016). "Racial Discrimination in the Sharing Economy: Evidence from a Field Experiment". Harvard Business School. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from Racial Discrimination in the Sharing Economy: Evidence from a Field Experiment
- ↑ "Airbnb Bans Trump Supporter for Canceling Asian Guest's Reservation." Fox News. FOX News Network, 7 Apr. 2017. Web. 13 Apr. 2017. <http://www.foxnews.com/travel/2017/04/07/airbnb-bans-trump-supporter-for-canceling-asian-guest-s-reservation.htm>.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 McGee, C. (2017). "How Airbnb's redesign aims to combat discrimination on the service". CNBC. Retrieved 10 April 2017, from http://www.cnbc.com/2017/04/07/airbnb-experimenting-with-site-design-to-fight-discrimination.html
- ↑ Rahman, K (2017). "Scammers using fake Airbnb listings dupe tourists". Daily Mail Australia. Retrieved 19 April 2017, from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-4239456/Scammers-using-fake-Airbnb-listings-dupe-tourists.html
- ↑ How to Get Landlord Permission to Host on Airbnb http://learnairbnb.com/airbnb-landlord-permission-negotiation/
- ↑ Host is subletting without landlord's permission https://community.withairbnb.com/t5/Travelers/Host-is-subletting-without-landlord-s-permission-will-I-the/td-p/196171