Difference between revisions of "Social Networking"
m (→Fake Profiles) |
(→List of Popular Social Networks) |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{box||[[File: Social-networking.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Pictured here are some of the more popular social networking sites. ]]}} | {{box||[[File: Social-networking.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Pictured here are some of the more popular social networking sites. ]]}} | ||
| − | '''Social Networking''' involve online tools that are used for communication, collaboration, and sharing thoughts of individuals | + | '''Social Networking''' involve online tools that are used for communication, collaboration, and sharing thoughts of individuals among friends. The popularity of these services continues to grow today, especially with younger generations of college students. People can post a large amount of information including personal identification, images, videos, music, and thoughts. Issues of privacy tend to be the main point of debate against these types of services since online identity can be extremely difficult to distinguish from one's offline identity. Social networking sites also make it easier for bullying to occur, as a user may easily remain anonymous. |
| + | |||
| + | Moral issues include cyber-bullying, fake profiles, and invasion of privacy. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | Social networking services started in the late 1990s, with a limited number of users. The types of information that could be displayed were small, and most of the services were closed off to a certain demographic of people. Most users were considered early adopters | + | Social networking services started in the late 1990s, with a limited number of users. The types of information that could be displayed were small, and most of the services were closed off to a certain demographic of people. Most users were considered early adopters of technology. |
The first reported social networking service was SixDegrees.com. This site allowed users to create profiles, add friends by common interests/groups, and browse through those lists. Many other sites began to pop-up, the next big ones to be Friendster in 2002 and then MySpace in 2003. In 2003 the professional social networking site LinkedIn was launched - to date LinkedIn was the first American social-networking company to list an IPO. However, social-networking took a big leap forward with the launch of [[Facebook]] in 2004. Just a year later Facebook expanded to include high-school students, and in 2006 expanded to include anyone 13 years or older. Facebook then began its domination in social networking service users year after year. The micro-blogging service [[Twitter]] launched in 2006. In 2011 Google launched it's social network Google+ and it became the quickest growing social-network ever and it added over 10 million users in less than a month<ref name="ref>[http://techcrunch.com/2011/07/27/google-minus/ Sophomore Slump? One Month In, Google+ Sees A Traffic Minus]</ref>. Even though some of the earlier sites lost users because of new features offered on new products, the general theme of the services remained the same. Each site allows a user to form a profile, with whatever amount of information they wish, and then to connect with other friends and family members to share thoughts, stories, or any other interests. | The first reported social networking service was SixDegrees.com. This site allowed users to create profiles, add friends by common interests/groups, and browse through those lists. Many other sites began to pop-up, the next big ones to be Friendster in 2002 and then MySpace in 2003. In 2003 the professional social networking site LinkedIn was launched - to date LinkedIn was the first American social-networking company to list an IPO. However, social-networking took a big leap forward with the launch of [[Facebook]] in 2004. Just a year later Facebook expanded to include high-school students, and in 2006 expanded to include anyone 13 years or older. Facebook then began its domination in social networking service users year after year. The micro-blogging service [[Twitter]] launched in 2006. In 2011 Google launched it's social network Google+ and it became the quickest growing social-network ever and it added over 10 million users in less than a month<ref name="ref>[http://techcrunch.com/2011/07/27/google-minus/ Sophomore Slump? One Month In, Google+ Sees A Traffic Minus]</ref>. Even though some of the earlier sites lost users because of new features offered on new products, the general theme of the services remained the same. Each site allows a user to form a profile, with whatever amount of information they wish, and then to connect with other friends and family members to share thoughts, stories, or any other interests. | ||
==Today== | ==Today== | ||
| − | Social networking services have become an integral part of everyday life. The sites are popular for sharing images, videos, stories, and other friendly information across groups of friends. They are also useful for staying in touch with friends and family who may live in another state or attend another school. | + | Social networking services have become an integral part of everyday life. The sites are popular for sharing images, videos, stories, and other friendly information across groups of friends. They are also useful for staying in touch with friends and family who may live in another state or attend another school. Users find information about current and local events, and many businesses rely on these platforms to advertise their products and services. Facebook, the largest of these networks, claims to have over 800 million active users, with 50% of these users logging in daily. Controversy surrounds the site, as far as privacy issues and other psychological issues that may result from use of social networking services. |
==List of Popular Social Networks== | ==List of Popular Social Networks== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
|style="width: 10%"|Membership | |style="width: 10%"|Membership | ||
|style="width: 10%"|Users | |style="width: 10%"|Users | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Facebook]]''' | |'''[[Facebook]]''' | ||
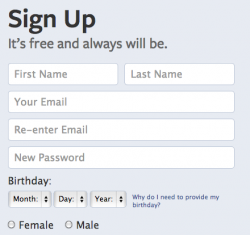
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Facebook|Facebook]] is the most popular social networking site available to Internet users today. Users must have an email address to join the site. Each user has a profile that can be made as private or public as desired and can include as much information as the user would like. On one's profile, photo albums, tagged photos, timeline posts, and status updates are viewable to others. |
| + | |[[File:Screen_shot_2012-12-11_at_11.49.42_PM.png|250px|thumb|left| An email address, rather than a username, is required to sign up.]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 45: | Line 42: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Foursquare''' | |'''Foursquare''' | ||
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Foursquare|Foursquare]] is a location-based networking site that allows users to "check-in" at various locations. The site is operated from a mobile device and has GPS tracking software, so the user has access to a list of nearby locations whenever they wish to "check-in." With each "check-in," users receive points and eventually reach different levels. |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 57: | Line 54: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[LinkedIn]]''' | |'''[[LinkedIn]]''' | ||
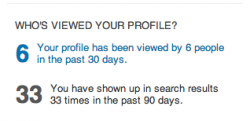
| − | |[[ | + | |[[LinkedIn|LinkedIn]] is a professional networking site in which users create profiles that include their education and work experience information. Users are able to directly message other users. One feature that differs from other social networking sites is the ability for users to see who has viewed their profile. Users are able to easily share their resumes with education, work experience, and community involvement, with other users or companies. LinkedIn allows users to cultivate a network with other working professionals to increase job opportunities in the future. By allowing users within the LinkedIn community to see who has viewed specific online profiles, the goal is to increase and foster relationships that potentially lead to new employment opportunities. |
| + | |[[File:Screen_shot_2012-12-11_at_11.41.20_PM.png|250px|thumb|left| The feature enabling users to see who has viewed their profile]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 63: | Line 61: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''MySpace''' | |'''MySpace''' | ||
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Myspace|Myspace]] is a social networking site in which users create profiles with pictures and customized backgrounds and music that plays whenever the user's page is refreshed. Users had the ability to write on other Myspace users' profiles and directly message them as well. |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 75: | Line 73: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Tumblr]]''' | |'''[[Tumblr]]''' | ||
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Tumblr|Tumblr]] is a blogging website where users post images and blog posts. Users can follow each other, as well as reblog content from another blog. Users generally blog and reblog pictures, although text is also common. |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 81: | Line 79: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Twitter]]''' | |'''[[Twitter]]''' | ||
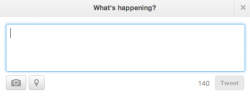
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Twitter|Twitter]] is a social networking site in which users post status updates in 140 characters or fewer. Users "follow" one another and the "tweets" of those accounts that one follows appears on their Twitter newsfeed. Twitter allows users to cultivate online relationships that can lead to a number of different opportunities, such as: increased contact, or closeness, with celebrities; faster breaking news sources; or the ability to connect with friends and colleagues in an online environment. |
| + | |[[File:Screen shot 2012-12-11 at 11.44.22 PM.png|250px|thumb|left| The box users view when composing a tweet; the "140" in the bottom right corner notifies users how many characters they have left to use.]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 87: | Line 86: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Pinterest]]''' | |'''[[Pinterest]]''' | ||
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Pinterest|Pinterest]] lets users create their personalized profile with "boards" specific to their interests. The user can add sites to each board, either by personal searching or by "pinning" another user's sites to their own. |
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 93: | Line 92: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''[[Instagram]]''' | |'''[[Instagram]]''' | ||
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Instagram|Instagram]] is the newest social networking site available to users with smartphones only. Instagram allows users to edit and post photos with a caption, tag other Instagram users, and geotag one's location. Users can follow one another, "like" photos, and leave comments on photos. |
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''[[Snapchat]]''' | ||
| + | |[[Snapchat|Snapchat]] is an app for iOS devices and Android devices where users can create images or videos that have a maximum duration of 10 seconds. Once the image or video is opened by another user, it disappears. Users can also add these images and videos to their "Snapchat Stories", where the post will be on the app under their name for 24 hours. | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
==Use of Social Networks by Businesses== | ==Use of Social Networks by Businesses== | ||
| − | Businesses have placed an emphasis on social networks as a means of marketing. The three most popular social networks for business use are [[Facebook]], [[Twitter]], and Google+. Social network marketing has grown extremely rapidly over the past decade, so much that 94% of all businesses that have a marketing department use social media. In addition 54% of those businesses who have used social media for over 3 years | + | Businesses have placed an emphasis on social networks as a means of marketing. The three most popular social networks for business use are [[Facebook]], [[Twitter]], and Google+. Social network marketing has grown extremely rapidly over the past decade, so much that 94% of all businesses that have a marketing department use social media. In addition, 54% of those businesses who have used social media for over 3 years have reported an increase in sales of that time period.<ref>[http://www.forbes.com/sites/moneywisewomen/2012/08/08/the-developing-role-of-social-media-in-the-modern-business-world/ The Developing Role of Social Media in the Modern Business World]</ref> |
==Ethical Issues== | ==Ethical Issues== | ||
| − | Many people argue social networking and other [[Web 2.0]] websites create many ethical concerns. Suddenly, information that was intended to be private, or shared among an intimate group of people is accessible by complete strangers. Individual rights issues can potentially arise as far as what content is viewable and by who is difficult for individuals to control. Our idea of what is right to share and who to share it with becomes hazy in an online, social environment. Issues such as [[Cyberbullying|cyber-bullying]], online stalking, [[Troll|trolling]] and other malicious behavior is hard to monitor within social networking services, as it is easy for a user to create a false profile or impersonate another person. There is not confirmation of identity | + | Many people argue social networking and other [[Web 2.0]] websites create many ethical concerns. Suddenly, information that was intended to be private, or shared among an intimate group of people is accessible by complete strangers. Individual rights issues can potentially arise as far as what content is viewable and by who is difficult for individuals to control. Our idea of what is right to share and who to share it with becomes hazy in an online, social environment. Issues such as [[Cyberbullying|cyber-bullying]], online stalking, [[Troll|trolling]] and other malicious behavior is hard to monitor within social networking services, as it is easy for a user to create a false profile or impersonate another person. There is not confirmation of identity unless there is a connection to the real world. Ethics surrounding the common good of all people is also an issue. Some user might join the site to create a group and connect with people for good causes, such as cancer awareness or to promote good qualities. It would be just as easy for a user to create a group for such bad actions as well. Questions of honesty and accountability are present in these services as well. Because little information is needed to confirm the accuracy on a user's profile, a person can get away with saying anything about themselves in order to connect to the people they want to be associated with. [[Anonymous Behavior in Virtual Environments|Anonymity]] is a large problem underlying all of these issues because there is a lack of accountability in social networks. |
===Privacy=== | ===Privacy=== | ||
| − | + | With a large network of people on the web, social networking services find their privacy policies under attack on a daily basis. Bits of data are being collected, collated, distributed, and stored constantly. <ref> Shoemaker, David W. “Self-Exposure and Exposure of the Self: Informational Privacy and the Presentation of Identity.” Ethics and Information Technology, vol. 12, no. 1, 2009, pp. 3–15., doi:10.1007/s10676-009-9186-x. </ref> Based on Shoemakers theories, the efforts of privacy of information can be controlled and limited. Control theory allows the user themselves to oversee the amount of information that they would like to share their social networking community. Users now assume responsibility for the information that is being posted. Limitation theory allows users to limit and restrict to whom is receiving their information. <ref> Shoemaker, David W. “Self-Exposure and Exposure of the Self: Informational Privacy and the Presentation of Identity.” Ethics and Information Technology, vol. 12, no. 1, 2009, pp. 3–15., doi:10.1007/s10676-009-9186-x. </ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | College students are finding they have to limit their privacy settings for their online pictures. Companies are starting to evaluate candidates through Facebook, LinkedIn, and other social networking sites. In order to maintain a level of privacy for their pictures containing alcohol and other deterrents that would steer potential employers away from hiring candidates, students and professionals are learning how to manage privacy settings on their social networking accounts quickly. The dilemma of accountability for managing privacy settings on social networking sites then falls on both the creators and members of the network. Social networking sites are implementing more innovative privacy settings daily in order to allow users to control the visibility of their profiles. | ||
===Cyber-bullying=== | ===Cyber-bullying=== | ||
| − | A variety of methods of [[Cyberbullying]] exist and are employed in social networks online. | + | A variety of methods of [[Cyberbullying|cyberbullying]] exist and are employed in social networks online. This is becoming a problematic issue, as many lawsuits and even life-threatening issues have arisen from cyberbullying via social media. There have been many instances where people have taken their own lives, or the lives of others, because of comments or threats made online.<ref>Huffington Post article on recent cyberbullying suicides [http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/29/erin-gallagher-irish-teen-commits-suicide-battle-cyberbullying_n_2040850.html http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/29/erin-gallagher-irish-teen-commits-suicide-battle-cyberbullying_n_2040850.html]</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | An example of an extreme effect of cyberbullying can be found in the case of [[Suicide of Amanda Todd|Amanda Todd]]. Amanda Todd was a 15-year-old Canadian girl who was bullied over the Internet for her decision to bare her breasts on camera to a stranger. This bullying took such a toll on her that she ultimately ended up taking her own life. This caused criticism of Canada's bullying legislation, and many people began to insist that cyberbullying be criminalized. <ref>Miceli, Karen. [http://www.insidehalton.com/opinion-story/4328944-canada-long-overdue-for-legislation-criminalizing-cyberbullying/|Canada long overdue for legislation criminalizing cyberbullying]. 22 January 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2017.</ref> | ||
===Fake Profiles=== | ===Fake Profiles=== | ||
| − | Fake profiles have become | + | Fake profiles have become prevalent as more prominent figures enter the social networking sphere. Across different platforms, there are many different levels of impersonation or fake accounts because the different sites require different levels of user authentication. Twitter is a hotbed for fake accounts, as there is little to no defense against it. In fact, many fake, or parody, accounts are some of the most popular out there. For example, there is a fake [[Wikipedia:Will Ferrell|Will Ferrell]] account that has accumulated nearly two million followers.<ref>@FillWerrell [https://twitter.com/FillWerrell https://twitter.com/FillWerrell]</ref> Many sites only require an e-mail address, which does not have to be an active one. Many people create fake or temporary addresses solely for the purpose of signing up for social media accounts. Twitter does verify certain high-profile accounts, but not all of them, so it is sometimes difficult to tell which accounts are authentic, and which are not. |
| + | |||
| + | On other sites, it is more difficult to create such accounts. One example is Google+. On Google+, users are required to register under their own names and cannot change that. Twitter also enacts methods that "verify" persons they feel have a high risk of impersonation.<ref>https://support.twitter.com/articles/119135-faqs-about-verified-accounts</ref> This makes it so that there is a distinction between those fake profiles and real ones. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Many people create fake accounts with negative intentions. This is not true for everyone, however, as many fake accounts serve to entertain (such as the aforementioned Will Ferrell account). These accounts might be made with good intentions, but could still offend others, regardless of the creator's intent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Facebook Depression === | ||
| + | Facebook Depression is a term coined for all social media accounts, originating from the website Facebook, for when teens or adolescence spend a large time on social media and begin to exhibit symptoms of depression. <ref> O'Keeffe, Gwenn Schurgin. "The Impact of Social Media on Children, Adolescents, and Families." Pediatrics From the American Academy of Pediatrics 127.4 (April 2011): n. pag. Web. </ref>. Acceptance by their friends and classmates are important to young adults and the rise of social media can trigger negative feelings towards oneself and even clinical depression. When teenagers see their friends posting pictures or hanging out without them they can experience the Fear of Missing Out, also known as FOMO, which can lead to feelings of sadness and loneliness. FOMO can lead to increased reliance on social media, leading to even more emotional issues. <ref>Fear of missing out, need for touch, anxiety, and depression are related to problematic smartphone use</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Identity=== | ||
| + | Online identity represents a form of "truth" about a user. Online identities are manufactured by through primary elements of pictures, profile biographies, and privacy settings. Other elements include their subscriber's behaviors, tagged photos, and advertisements that track behavior. | ||
| + | Each site has their own purpose and means of building relationships online. LinkedIn intends to build a professional community online while Facebook intends to build a friendly community online. | ||
| + | Based on the site's environment, it will dictate how and what a user publishes their information to their communities. The user limitation hides pieces of information from themselves from site to site in an effort to present themselves that aligns with the purpose of the platform. <ref> Shoemaker, David W. “Self-Exposure and Exposure of the Self: Informational Privacy and the Presentation of Identity.” Ethics and Information Technology, vol. 12, no. 1, 2009, pp. 3–15., doi:10.1007/s10676-009-9186-x. </ref> With these limitations, a user's authentic self will never be achieved online. <ref> Smith and Watson, “Virtually Me: A Toolbox about Online Self-Presentation,” 2012. </ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Fake News=== | |
| + | Fake news is the act of spreading false information through social networking sites. <ref> “Definition of ‘Fake News’ - English Dictionary.” Fake News Definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary, dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/fake-news. </ref> These posts by users are often not credible but easily believed due to sharing similar political and other social views. This trend has intensified over the past year with the growth of social media power and influence. Posts can reach thousands to millions of people within hours with confirmation bias. It is easy on each networking site to affirm a user's post by liking or retweeting. <ref> Law, Tom. “Ethics in the News .” Ethical Journalism Network, Ethical Journalism Network, 19 Jan. 2017, ethicaljournalismnetwork.org/resources/publications/ethics-in-the-news/fake-news. </ref> | ||
| + | These actions have caused much political turmoil in the 2016 Presidential Election. | ||
==Future== | ==Future== | ||
| − | The future of social networking services remains to be unknown, but new innovations are being created on a daily basis as far as how big the social networks can get. Connecting to friends, employers, and family | + | The future of social networking services remains to be unknown, but new innovations are being created on a daily basis as far as how big the social networks can get. Connecting to friends, employers, and family is good, but joining together for awareness on hot topic issues, put beside a page where friends can decide where they want to eat together just hints at the enormity the services can have. There will no doubt be more of these services created, especially to individualized interests, as people try to keep parts of their lives separate. |
===The Stop Online Privacy Act=== | ===The Stop Online Privacy Act=== | ||
| − | Under the SOPA, the entire future of social networking websites could be at risk. Due to the high volume of constant user submission (especially on the larger-scale websites like Facebook), it is theoretically possible that if just one of those submissions contained a link to an illegal download the entire website could be shut down<ref>[http://www.dailydot.com/politics/reddit-alexis-ohanian-stop-online-piracy-act/ Reddit cofounder pleads case against the Stop Online Piracy Act]</ref>. The implications for the economy of a website like Facebook, which hosts thousands of third-party apps and is quickly becoming the primary mode of distribution for many businesses who operate through social network-mediated apps, being shut down could be disastrous. | + | Under the SOPA, the entire future of social networking websites could be at risk. Due to the high volume of constant user submission (especially on the larger-scale websites like Facebook), it is theoretically possible that if just one of those submissions contained a link to an illegal download the entire website could be shut down<ref>Morris, Kevin. "Reddit Cofounder Speaks out against the Stop Online Piracy Act." The Daily Dot. N.p., 26 Mar. 2019. Web. [http://www.dailydot.com/politics/reddit-alexis-ohanian-stop-online-piracy-act/ Reddit cofounder pleads case against the Stop Online Piracy Act]</ref>. The implications for the economy of a website like Facebook, which hosts thousands of third-party apps and is quickly becoming the primary mode of distribution for many businesses who operate through social network-mediated apps, being shut down could be disastrous. |
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Latest revision as of 00:41, 29 April 2019
Social Networking involve online tools that are used for communication, collaboration, and sharing thoughts of individuals among friends. The popularity of these services continues to grow today, especially with younger generations of college students. People can post a large amount of information including personal identification, images, videos, music, and thoughts. Issues of privacy tend to be the main point of debate against these types of services since online identity can be extremely difficult to distinguish from one's offline identity. Social networking sites also make it easier for bullying to occur, as a user may easily remain anonymous.
Moral issues include cyber-bullying, fake profiles, and invasion of privacy.
Contents
History
Social networking services started in the late 1990s, with a limited number of users. The types of information that could be displayed were small, and most of the services were closed off to a certain demographic of people. Most users were considered early adopters of technology.
The first reported social networking service was SixDegrees.com. This site allowed users to create profiles, add friends by common interests/groups, and browse through those lists. Many other sites began to pop-up, the next big ones to be Friendster in 2002 and then MySpace in 2003. In 2003 the professional social networking site LinkedIn was launched - to date LinkedIn was the first American social-networking company to list an IPO. However, social-networking took a big leap forward with the launch of Facebook in 2004. Just a year later Facebook expanded to include high-school students, and in 2006 expanded to include anyone 13 years or older. Facebook then began its domination in social networking service users year after year. The micro-blogging service Twitter launched in 2006. In 2011 Google launched it's social network Google+ and it became the quickest growing social-network ever and it added over 10 million users in less than a month[1]. Even though some of the earlier sites lost users because of new features offered on new products, the general theme of the services remained the same. Each site allows a user to form a profile, with whatever amount of information they wish, and then to connect with other friends and family members to share thoughts, stories, or any other interests.
Today
Social networking services have become an integral part of everyday life. The sites are popular for sharing images, videos, stories, and other friendly information across groups of friends. They are also useful for staying in touch with friends and family who may live in another state or attend another school. Users find information about current and local events, and many businesses rely on these platforms to advertise their products and services. Facebook, the largest of these networks, claims to have over 800 million active users, with 50% of these users logging in daily. Controversy surrounds the site, as far as privacy issues and other psychological issues that may result from use of social networking services.
List of Popular Social Networks
| Name | Focus | Features | Membership | Users | |
| Facebook is the most popular social networking site available to Internet users today. Users must have an email address to join the site. Each user has a profile that can be made as private or public as desired and can include as much information as the user would like. On one's profile, photo albums, tagged photos, timeline posts, and status updates are viewable to others. | |||||
| Flickr | Flickr is an online community that enables users to post images and videos for both their own personal use and to share with other users. Flickr offers its users both free and pro accounts. Free accounts let users upload up to 300 MB of photos while a pro account has unlimited space.[2] | ||||
| Friendster | Friendster is considered the original social networking site. Each user has a profile and is able to share content and communicate with other Friendster users. | ||||
| Foursquare | Foursquare is a location-based networking site that allows users to "check-in" at various locations. The site is operated from a mobile device and has GPS tracking software, so the user has access to a list of nearby locations whenever they wish to "check-in." With each "check-in," users receive points and eventually reach different levels. | ||||
| Google+ | Google+ is a an embedded social networking site within Google in which users much have a gmail account to create a profile. What makes Google+ unique is the site's ability to let users organize other Google+ users into "circle" or "hangouts." For instance, a user may have a "Friends", "Family", and "Coworkers" circle. | ||||
| LinkedIn is a professional networking site in which users create profiles that include their education and work experience information. Users are able to directly message other users. One feature that differs from other social networking sites is the ability for users to see who has viewed their profile. Users are able to easily share their resumes with education, work experience, and community involvement, with other users or companies. LinkedIn allows users to cultivate a network with other working professionals to increase job opportunities in the future. By allowing users within the LinkedIn community to see who has viewed specific online profiles, the goal is to increase and foster relationships that potentially lead to new employment opportunities. | |||||
| MySpace | Myspace is a social networking site in which users create profiles with pictures and customized backgrounds and music that plays whenever the user's page is refreshed. Users had the ability to write on other Myspace users' profiles and directly message them as well. | ||||
| StumbleUpon | StumbleUpon recommends pages to users based on their previously noted interests in specific topics and categories. In the upper left-hand corner of the site, there is a button "Stumble!" which users press and the site randomly generates pages based on their interests. Users can rate pages as "like" or "unlike" which will further let the site know which pages to generate for the user. | ||||
| Tumblr | Tumblr is a blogging website where users post images and blog posts. Users can follow each other, as well as reblog content from another blog. Users generally blog and reblog pictures, although text is also common. | ||||
| Twitter is a social networking site in which users post status updates in 140 characters or fewer. Users "follow" one another and the "tweets" of those accounts that one follows appears on their Twitter newsfeed. Twitter allows users to cultivate online relationships that can lead to a number of different opportunities, such as: increased contact, or closeness, with celebrities; faster breaking news sources; or the ability to connect with friends and colleagues in an online environment. | |||||
| Pinterest lets users create their personalized profile with "boards" specific to their interests. The user can add sites to each board, either by personal searching or by "pinning" another user's sites to their own. | |||||
| Instagram is the newest social networking site available to users with smartphones only. Instagram allows users to edit and post photos with a caption, tag other Instagram users, and geotag one's location. Users can follow one another, "like" photos, and leave comments on photos. | |||||
| Snapchat | Snapchat is an app for iOS devices and Android devices where users can create images or videos that have a maximum duration of 10 seconds. Once the image or video is opened by another user, it disappears. Users can also add these images and videos to their "Snapchat Stories", where the post will be on the app under their name for 24 hours. |
Use of Social Networks by Businesses
Businesses have placed an emphasis on social networks as a means of marketing. The three most popular social networks for business use are Facebook, Twitter, and Google+. Social network marketing has grown extremely rapidly over the past decade, so much that 94% of all businesses that have a marketing department use social media. In addition, 54% of those businesses who have used social media for over 3 years have reported an increase in sales of that time period.[3]
Ethical Issues
Many people argue social networking and other Web 2.0 websites create many ethical concerns. Suddenly, information that was intended to be private, or shared among an intimate group of people is accessible by complete strangers. Individual rights issues can potentially arise as far as what content is viewable and by who is difficult for individuals to control. Our idea of what is right to share and who to share it with becomes hazy in an online, social environment. Issues such as cyber-bullying, online stalking, trolling and other malicious behavior is hard to monitor within social networking services, as it is easy for a user to create a false profile or impersonate another person. There is not confirmation of identity unless there is a connection to the real world. Ethics surrounding the common good of all people is also an issue. Some user might join the site to create a group and connect with people for good causes, such as cancer awareness or to promote good qualities. It would be just as easy for a user to create a group for such bad actions as well. Questions of honesty and accountability are present in these services as well. Because little information is needed to confirm the accuracy on a user's profile, a person can get away with saying anything about themselves in order to connect to the people they want to be associated with. Anonymity is a large problem underlying all of these issues because there is a lack of accountability in social networks.
Privacy
With a large network of people on the web, social networking services find their privacy policies under attack on a daily basis. Bits of data are being collected, collated, distributed, and stored constantly. [4] Based on Shoemakers theories, the efforts of privacy of information can be controlled and limited. Control theory allows the user themselves to oversee the amount of information that they would like to share their social networking community. Users now assume responsibility for the information that is being posted. Limitation theory allows users to limit and restrict to whom is receiving their information. [5]
College students are finding they have to limit their privacy settings for their online pictures. Companies are starting to evaluate candidates through Facebook, LinkedIn, and other social networking sites. In order to maintain a level of privacy for their pictures containing alcohol and other deterrents that would steer potential employers away from hiring candidates, students and professionals are learning how to manage privacy settings on their social networking accounts quickly. The dilemma of accountability for managing privacy settings on social networking sites then falls on both the creators and members of the network. Social networking sites are implementing more innovative privacy settings daily in order to allow users to control the visibility of their profiles.
Cyber-bullying
A variety of methods of cyberbullying exist and are employed in social networks online. This is becoming a problematic issue, as many lawsuits and even life-threatening issues have arisen from cyberbullying via social media. There have been many instances where people have taken their own lives, or the lives of others, because of comments or threats made online.[6]
An example of an extreme effect of cyberbullying can be found in the case of Amanda Todd. Amanda Todd was a 15-year-old Canadian girl who was bullied over the Internet for her decision to bare her breasts on camera to a stranger. This bullying took such a toll on her that she ultimately ended up taking her own life. This caused criticism of Canada's bullying legislation, and many people began to insist that cyberbullying be criminalized. [7]
Fake Profiles
Fake profiles have become prevalent as more prominent figures enter the social networking sphere. Across different platforms, there are many different levels of impersonation or fake accounts because the different sites require different levels of user authentication. Twitter is a hotbed for fake accounts, as there is little to no defense against it. In fact, many fake, or parody, accounts are some of the most popular out there. For example, there is a fake Will Ferrell account that has accumulated nearly two million followers.[8] Many sites only require an e-mail address, which does not have to be an active one. Many people create fake or temporary addresses solely for the purpose of signing up for social media accounts. Twitter does verify certain high-profile accounts, but not all of them, so it is sometimes difficult to tell which accounts are authentic, and which are not.
On other sites, it is more difficult to create such accounts. One example is Google+. On Google+, users are required to register under their own names and cannot change that. Twitter also enacts methods that "verify" persons they feel have a high risk of impersonation.[9] This makes it so that there is a distinction between those fake profiles and real ones.
Many people create fake accounts with negative intentions. This is not true for everyone, however, as many fake accounts serve to entertain (such as the aforementioned Will Ferrell account). These accounts might be made with good intentions, but could still offend others, regardless of the creator's intent.
Facebook Depression
Facebook Depression is a term coined for all social media accounts, originating from the website Facebook, for when teens or adolescence spend a large time on social media and begin to exhibit symptoms of depression. [10]. Acceptance by their friends and classmates are important to young adults and the rise of social media can trigger negative feelings towards oneself and even clinical depression. When teenagers see their friends posting pictures or hanging out without them they can experience the Fear of Missing Out, also known as FOMO, which can lead to feelings of sadness and loneliness. FOMO can lead to increased reliance on social media, leading to even more emotional issues. [11]
Identity
Online identity represents a form of "truth" about a user. Online identities are manufactured by through primary elements of pictures, profile biographies, and privacy settings. Other elements include their subscriber's behaviors, tagged photos, and advertisements that track behavior. Each site has their own purpose and means of building relationships online. LinkedIn intends to build a professional community online while Facebook intends to build a friendly community online. Based on the site's environment, it will dictate how and what a user publishes their information to their communities. The user limitation hides pieces of information from themselves from site to site in an effort to present themselves that aligns with the purpose of the platform. [12] With these limitations, a user's authentic self will never be achieved online. [13]
Fake News
Fake news is the act of spreading false information through social networking sites. [14] These posts by users are often not credible but easily believed due to sharing similar political and other social views. This trend has intensified over the past year with the growth of social media power and influence. Posts can reach thousands to millions of people within hours with confirmation bias. It is easy on each networking site to affirm a user's post by liking or retweeting. [15] These actions have caused much political turmoil in the 2016 Presidential Election.
Future
The future of social networking services remains to be unknown, but new innovations are being created on a daily basis as far as how big the social networks can get. Connecting to friends, employers, and family is good, but joining together for awareness on hot topic issues, put beside a page where friends can decide where they want to eat together just hints at the enormity the services can have. There will no doubt be more of these services created, especially to individualized interests, as people try to keep parts of their lives separate.
The Stop Online Privacy Act
Under the SOPA, the entire future of social networking websites could be at risk. Due to the high volume of constant user submission (especially on the larger-scale websites like Facebook), it is theoretically possible that if just one of those submissions contained a link to an illegal download the entire website could be shut down[16]. The implications for the economy of a website like Facebook, which hosts thousands of third-party apps and is quickly becoming the primary mode of distribution for many businesses who operate through social network-mediated apps, being shut down could be disastrous.
See Also
- Experience Project
- Privacy in Social Networking
- Social Networking Services
- Online Dating
- Spotify
External Links
References
- ↑ Sophomore Slump? One Month In, Google+ Sees A Traffic Minus
- ↑ Flickr
- ↑ The Developing Role of Social Media in the Modern Business World
- ↑ Shoemaker, David W. “Self-Exposure and Exposure of the Self: Informational Privacy and the Presentation of Identity.” Ethics and Information Technology, vol. 12, no. 1, 2009, pp. 3–15., doi:10.1007/s10676-009-9186-x.
- ↑ Shoemaker, David W. “Self-Exposure and Exposure of the Self: Informational Privacy and the Presentation of Identity.” Ethics and Information Technology, vol. 12, no. 1, 2009, pp. 3–15., doi:10.1007/s10676-009-9186-x.
- ↑ Huffington Post article on recent cyberbullying suicides http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/29/erin-gallagher-irish-teen-commits-suicide-battle-cyberbullying_n_2040850.html
- ↑ Miceli, Karen. long overdue for legislation criminalizing cyberbullying. 22 January 2014. Retrieved 13 April 2017.
- ↑ @FillWerrell https://twitter.com/FillWerrell
- ↑ https://support.twitter.com/articles/119135-faqs-about-verified-accounts
- ↑ O'Keeffe, Gwenn Schurgin. "The Impact of Social Media on Children, Adolescents, and Families." Pediatrics From the American Academy of Pediatrics 127.4 (April 2011): n. pag. Web.
- ↑ Fear of missing out, need for touch, anxiety, and depression are related to problematic smartphone use
- ↑ Shoemaker, David W. “Self-Exposure and Exposure of the Self: Informational Privacy and the Presentation of Identity.” Ethics and Information Technology, vol. 12, no. 1, 2009, pp. 3–15., doi:10.1007/s10676-009-9186-x.
- ↑ Smith and Watson, “Virtually Me: A Toolbox about Online Self-Presentation,” 2012.
- ↑ “Definition of ‘Fake News’ - English Dictionary.” Fake News Definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary, dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/fake-news.
- ↑ Law, Tom. “Ethics in the News .” Ethical Journalism Network, Ethical Journalism Network, 19 Jan. 2017, ethicaljournalismnetwork.org/resources/publications/ethics-in-the-news/fake-news.
- ↑ Morris, Kevin. "Reddit Cofounder Speaks out against the Stop Online Piracy Act." The Daily Dot. N.p., 26 Mar. 2019. Web. Reddit cofounder pleads case against the Stop Online Piracy Act
http://jcmc.indiana.edu/vol13/issue1/boyd.ellison.html http://www.facebook.com/press/info.php?statistics http://edu.udym.com/ethics-of-social-networking/ http://www.scu.edu/ethics/publications/submitted/social-networking.html