Technological Singularity
Technological singularity is the theory of technology accelerating to the point of creating a superintelligence, which will exceed human intelligence. Several technologies are following this path, which include artificial intelligence, brain-computer interfaces, biological augmentations, genetic engineering, and nanotechnology. [2] Because of the unknown potential capabilities of such intelligence, technological singularity is very similar to its astronomical counterpart, a singularity in space (black hole). It is the definitive point in our future where a predictable path will lead to an unpredictable outcome.
John von Neumann was the first to use the term “singularity” in order to describe a specific moment in the history of the human race in which all human processes will become obsolete because of technological acceleration. The science fiction writer and mathematician, Vernor Vinge, then coined the term “technological singularity” in 1983 and argued that certain technologies, like artificial intelligence, will be the potential causes of the singularity. The concept is now becoming more popular through the efforts of futurist, singularitiarian, and co-founder of the Singularity University organization, Ray Kurzweil, as he tries to educate the masses about the future advancements in technology.
Kurzweil and other enthusiasts believe that the moment of the singularity will occur between 2020 and 2050, through the predictions that are based upon Moor’s Law and the trend of exponential growth in technology.[3]
Contents
History
Samuel Butler wrote in the 1863 “Darwin Among The Machines” letter, “Who will be man’s successor? To which the answer is: We are ourselves creating our own successors. Man will become to the machine what the horse and the dog are to man; the conclusion being that machines are, or are becoming, animate.”[2]
In the 1950’s, John von Neumann stated, “One conversation centered on the ever accelerating progress of technology and changes in the mode of human life, which gives the appearance of approaching some essential singularity in the history of the race beyond which human affairs, as we know them, could not continue.” He used the term singularity, but in the since of normal progress and not the creation of super intelligence.[4]
In 1965, I.J. Good, a British mathematician, emphasized on something that he called an “intelligence explosion”:[1]
- Let an ultraintelligent machine be defined as a machine that can far surpass all the intellectual activities of any man however clever. Since the design of machines is one of these intellectual activities, an ultraintelligent machine could design even better machines; there would then unquestionably be an "intelligence explosion," and the intelligence of man would be left far behind. Thus the first ultraintelligent machine is the last invention that man need ever make.
In 1983, Vernor Vinge, a mathematician and writer, coined the term technological singularity in his article for Omni magazine. He went on stating “We will soon create intelligences greater than our own. When this happens, human history will have reached a kind of singularity, an intellectual transition as impenetrable as the knotted space-time at the center of a black hole, and the world will pass far beyond our understanding.”[3][5]
Vernor Vinge went on using technological singularity as a major component in the novels, The Peace War (1984) and Marooned in Realtime (1986).
Hans Moravec, in 1988, published the book Mind Children that analyzed the progression of robotics through generalizing Moore’s Law. This lead to the conclusion that human intelligence will be exceeded by machines towards the first half of the 21st century. He explains a scenario in which robots will evolve into a new kind of artificial beings around 2030.
In 1993, Vernor Vinge presented the article “The Coming Technological Singularity: How to Survive in the Post-Human Era” to a NASA symposium that stated, “Within 30 years, we will have the technological means to create super-human intelligence. Shortly after, the human era will be ended.” He went on to describe his four possible igniters of the singularity as breakthrough achievements that will be dependable in large part to the improvements in computer hardware and with the rate of steady exponential progress in software as well. As Vinge continues, he brings up the notion of exponential progression beyond the initial achievements. For instance, Vinge writes, “…ideas themselves should spread ever faster, and even the most radical will quickly become commonplace.”[1][4]
Australian scholar Damien Broderick focused on the extreme impacts of the technological acceleration through the phases that were anticipated to occur within several decades. He published the work in his 1997 and 2001 books, which both were titled The Spike.
In 1999, Ray Kurzweil published his book, The Age of Spiritual Machines. This book was the first time Kurzweil proposed the “Laws of Accelerating Returns”, which is the perceived increase in the rate of technological progress through the extension of Moore’s Law to describe the exponential growth. It's the acceleration of the pace of and the exponential growth of the products of an evolutionary process. From the chaos and disorder, these laws develops options of diversity and the evolutionary process will then continually prune its choices to create ever greater order. [6]
In 2000, Bill joy expressed his concerns of the growing advances in many technologies and the risk they have on humanity in the publication of his article, “Why the future doesn’t need us”, in Wired Magazine. The argument presented went into detail of robotics replacing humanity.
In 2005, the book, The Singularity is Near, was published by futurist, Ray Kurzweil. His book included many in-depth analyses of technological singularity for several current technology branches. Mostly, the technologies that had his focus were the “three overlapping revolutions.” Kurzweil writes, “The first half of the twenty-first century will be characterized by three overlapping revolutions- in Genetics, Nanotechnology, and Robotics.” He continues by stating that we are currently in the Genetic revolution and through understanding the information processes underlying life, we are learning how to reengineer our own biology.[6]
As Kurzweil is labeled “the optimistic futurist”, his views bring in much criticism from the more defensive visionaries of singularity.
Robin Hanson referred to “singularity” as a extreme increase in economic growth. In 2008, Hanson proposes that the next economic singularity will boost the economy by 60 and 250 times, which could be triggered by finding a correct process to completely replace all human labor. Hason went on using the Industrial revolution as an example of a past singularity.[2]
Kurzweil and Peter Diamandis established the non-profit organization of Singularity University in 2009. The aim of the organization is to “assemble, educate and inspire a cadre of leaders who strive to understand and facilitate the development of exponentially advancing technologies and apply, focus and guide these tools to address humanity’s grand challenges.”[7]
How to Create a Mind: The Secret of Human Thought Revealed, Kurzweil’s newest book, was just released on November 13, 2012. He ends up exploring in great detail the potentials of artificial intelligence to increase human capabilities and the process of reverse-engineering the brain.[2]
Concept
Most enthusiasts define technological singularity as the period of time after technological creations exceed in computing power over human intellect. And in due process, when we have the capabilities to create these being that possesses greater intelligence, its stands to reason that they, or their near-descendants, will be able to create intelligent beings that exceed themselves.[3] Originally this term borrowed the word singularity from astrophysics, which it refers to a point in space-time that does not follow the rules of ordinary physics, like the center of a black hole. At this point in space-time, the physical quantities such as the gravitational field become infinite. This corresponds to the potential infinite possibilities that could occur in a post-technological singularity world because of the difficulty of predicting the intentions and capabilities of post-singularity technological entities.
Some writers tie in the concept of exponential growth into the observations of various technologies, while using Moore’s Law as the main example to explain such observations. This leaves predictions, Like Vinge’s and Kurzweil’s, that the technological singularity will occur at some point during the 21st century.[3]
Accelerating Change
Through the exploration of past trends and the shortening of the gaps between new technologies, there is a noticeable consistant growth in the acceleration of technologies, which believers use to back up the theory of singularity and the rather soon prediction of its occurrence.
Kurzweil first coined the “Laws of Accelerating Returns” in 1999. He took the concept of the exponential trend of Moore’s Law, which states that for every twenty-four months there will be a twice as many transistors on an integrated circuit, and applied that to various technologies.[6]
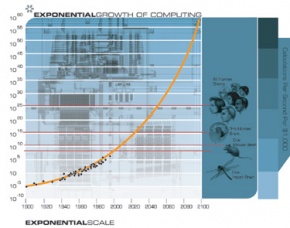
According to Kurzweil, when a technology comes to a roadblock in its exponential growth, a new technology will be invented to allow us to pass through that block. He takes it one step further by comparing exponential growth to evolution. Since the beginning of evolution, he states that more complex life forms have been evolving exponentially faster, with shorter intervals between each new emerging life form, who have the capacity to engineer new traits that replace the inefficient mechanisms of selection in evolution.[9]
The law of accelerating returns is fundamentally an economic theory. It's the economic imperative of a competitive market that is the main force behind the push that's making technology move forward. Survival is the biological evolution counterpart to economic imperative. Kurzweil has the example of machines that are more precise in carrying out their missions have increased value, which explains why they are being built in the first place.[6]
Kurzweil’s prediction of the singularity will occur in 2045 as the time he expects computer-based intelligence will exceed the total human brainpower[3], This prediction is due to a gradual ascent into singularity, rather than Vinge’s prediction of rapidly self-improving superhuman intelligence.
The technological singularity will supposably lead the our civilization in mastering all the resources of Earth. This type of civilization is known as "Kardashev Type I civilization" and was first developed by Nikolai Kardashev, a Soviet astronomer, in 1964.[6]
Superintelligence
An intelligence explosion, first used in 1965 by I.J Good, is a major concept in the technological singularity as it's a result from intelligent machines designing their next generation without human intervention.[10] All proposed methods of creating a superintellegence can fall underneath two areas of technology, artificial intelligence and human intelligence enhancement.
The turning point in intelligence acceleration depends on some factors. One factor deals with the dependency of new enhancements in intelligences on the previous generation of enhancements. Then the second factor is the process that each improvement has to be able to produce one or more improvements greater than its own abilities. This will help with the continuation of the singularity, but it will be potentially hard to keep consistent. Advancements in intelligence will most likely produce more complications in order to further the growth in technology. The third factor is the laws of physics. Improvements will eventually be hindered by the physical world.[2]
Artificial Intelligence
The development of a strong artificial intelligence, an AI that can learn and improve itself, will be based upon the principles of operation of human intelligence form reverse engineering all parts of the brain. [5][2]This process of reverse engineering has been predicted by many, like Ray Kurzweil, to be achievable through the brain-capable computing platforms that will exist in the 2020’s. This is thought to be the most important development that this century will see. It will mean that a creation of biology has finally mastered its own intelligence and discovered means to over come its limitations.
A big challenge in engineering strong AI, but yet the biggest benefit, will be development of the learning capabilities. This will allow AIs to be educated at a much faster rate compared to unenhanced humans, which will make years of learning into weeks. Some foreseen achievements include sufficient mastery of language and shared human knowledge to pass the Turning test, uploading the human brain, unmanned warfare, space exploration, and fast medical data mining.[5][2]
The relationship between strong AI and nanotechnology creates a “the chicken or the egg” phenomenon, in which either strong AI lead to full nanotechnology or full nanotechnology lead to strong AI. But because of limited intelligence nanotechnology actually needs, most predict the latter.[5]
Human Enhancement


Human enhancements, like intelligence amplifiers, have been theorized as the easiest path to achieve superintelligence rather than creating it, like pure artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence would benefit from a closer connection with biological life. Instead of simply trying to model and understand biological life with computers, research could be directed towards the creation of systems that rely on biological life for guidance. Also it will help fill in the gaps in our limited understanding of certain functions in which we don’t understand well enough yet to implement in software and hardware.[4]
There currently have been great achievements in human enhancements. This includes limb prosthetics, direct brain links, advancements in bandwidth through optic trunks, nanobot technology, and drugs and supplement advancements. [4]
For example, Dr. Ron Kahn, from the Joslin Diabetes Center, Has been making advancements in the biochemical field through drug and supplement research and experiments. He has identified and analyzed the “fat insulin receptor” (FIR) gene, which controls how much fat the fat cells in the body will store. Through the experiements with a FIR knockout drug, the test mice lived around 18% longer and had lower rates of heart disease and diabetes.[5]
Implementing nanotechnology into our bodies will help regulate our bodily functions, like our digestive system, by extracting the right nutrients we need, order the additional nutrients and supplements through our personal wireless nanobot network, and send the rest of matter on to be eliminated. There are many potential systems that can be created through nanotechnology for benefiting patients with certain diseases and deformities. For example, nanotehcnology to develop systems of delivering dopamine to the brain for Parkinsons’s patients, provide blood-clotting factors for patients with hemophilia, and deliver cancer fighting drugs directly to the correct sites.[5]
Existential Risks
Nick Bostrom coined the term “existential risks,” which are risks that we cannot address with complete assurance in any strategy that we have devised today.[5] These risks fall underneath the categories of global, profound, and terminal.
With the achievement of strong AI, the probable out-of-control growth through the readily advancements and powers to multiply brings up concerns about runaway artificial intelligence. One strong AI will immediately give rise to many other strong AI’s through the understanding and improving of their own design. This will lead to the rapid evolution of AI into yet a more intelligent AI, which then the cycle will repeat itself indefinitely.[5][2]
The rapid growth of strong AI creates a risk of “unfriendly AI.” This type of AI is left with no notion of ethical values and has the possibility of becoming unfriendly to biological humanity and its values. Because of the difficulty in developing a strong AI that will remain friendly through its many , designing an unfriendly AI is a high possibility. The risk of an unfriendly strong AI comes from the deep integration of the AI into our infrastructure through many diverse fields in which will utilize the AI. This means that on many different fronts, dangerous actions to harm biological humans will become dominate.
Eliezer Yudkowsky stated that we need to “get it right the first time,” and that its intitial design must have “zero nonrecoverable errors.” Yudkowsky has studied many ethical systems and architectures in order to help us prepare for the development of a strong AI that would be friendly. But because of the almost limitless possibilities of ethical decisions, there is much concern and likelihood of developing an unfriendly AI, even with Yudkowsky's analytical work, as we cannot see every outcome.[5]
In order to replicate, nanobots will most likely be based upon carbon and its unique four-way bonding, because as it’s an ideal building block for molecular entities. This creates a concern with potential defected nanotechnology as out of control nanobots will then seek out the most fundamental building block to biological life on Earth, carbon. And because nanotechnology requires trillions of devices in order to be useful, nanobot's replication process would potentially result in biological destruction. This attack on biological life is believed to happen through defection in the rapid exponential reproduction of nanotechnology and that reproduction will, at some point, create a mutation in the process and will birth a hazardous intelligence.
Criticism and Ethical Issues
Vinge stated in his 1993 article, "The problem is not that the Singularity represents simply the passing of humankind from center stage, but that it contradicts some of our most deeply held notions of being. I think a closer look at the notion of strong superhumanity can show why that is."[4]This touches base on a critical concern that deals with creating "life" from something that is not biological.
Another point Vinge bring up in his 1993 article is the concept of immortality. He states, "This "problem" about immortality comes up in much more direct ways. The notion of ego and self-awareness has been the bedrock of the hardheaded rationalism of the last few centuries. Yet now the notion of self-awareness is under attack from the Artificial Intelligence people ("self-awareness and other delusions")."[4] With the progress of technology after the singularity, there will be the ability to upload ones brain, in which he or she would be able to live on forever. Questions like "Will having my brain be uploaded still make me human?" and "How will society function without the biological human?" arise and will probably go unanswered until (if) we reach the singularity.
The digital divide, the division between the rich-poor and accessibility to technology, has been a concern with the coming of the technological singularity. These technologies might only be obtainable by the rich, which will leave the rest of humankind with uncertainty with what will happen.[5]
The Singularity brings criticism from holism, the theory of parts of a whole cannot be understood and exist without the whole, which they bring in the argument that parts of the human being, the conscious brain and behaviors, cannot be replicated do to the fundamental incorporation of such parts into reality of the human existence. This creates an ethical controversy, as the singularity will be the moment when biological processes and designs will be copied and surpassed by artificial organisms, which, by holistic values, is not possible by a non-biological being. Many critics from holistic backgrounds then will believe that machines will ever achieve human intelligence, because they are not human.
Schmidhuber suggested in 2006 that differences in memory of recent and distant events create an illusion of accelerating change, and that such phenomena may be responsible for past apocalyptic predictions. [2]
In Media
Television
The popular manga and Japanese animated series, Ghost in the Shell, follows the members of a special operations task-force and takes place in the year 2029. The ability to upload ones brain is a standard, as many people in this universe have become cyborgs with prosthetics bodies.[12]
The episode “The Cruciferous Vegetable Amplification” of the popular Television show The Big Bang Theory (season 4, episode 2) revolves around Sheldon Cooper trying to cope with mortality and the goal to experience the coming of the singularity.
Film

The 1950’s I, Robot book series published by Isaac Asimov, which also was the name of the 2004 movie based off of the books, featuring Will Smith, is a collection of nine science fiction short stories. These short stories included supercomputers managing the world’s economy and leading humanity to salvation without conflicts, aberrant behavior of robots, and Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics. [2][14]
The 2013 science fiction film, The Prototype, is about a military humanoid drone that escapes government containment, and has to survive while being on the run. The drone is a byproduct of Dr. Maxwell (Joseph Mawle) using himself as the first prototype. The movie revolves around the thesis written by Dr. Maxwell on how humans will evolve into machines. Check out the Prototype trailer here
The Matrix series(1999-2003) depicts a world in which computers and technology hit a point of superintelligence and violently overpower the human race. The collective machines farm the humans in pods for their bioelectricity and thermal energy, while keeping the humans in a virtual universe that resembles the 21st century. [15] Many movies and TV series, including the Terminator, Battlestar Galactica, and I, Robot(the movie), follow a similar plot line of computer intelligence domination.

Transcendent Man Documentary by Barry Ptolemy follows the life of Ray Kurzweil while he is trying to promote his ideas to the masses. This documentary brings to light his bold vision of the singularity. Besides informing the viewers of Kurzweil’s predictions and theories, it also depicted the critics view as they accused Ray of being too optimistic and argue that the dangers of singularity far outweigh the benefits. [17] Check out the Transcendent Man trailer here
Video Games
The famous Xbox 360 RPG video game series, Mass Effect, depicts a time of accelerated change, which has lead to efficient space travel, alien contact, and much advancement in human enhancements. The protagonist can decide to play with 6 variations of character abilities, which include technological advancements and telekinesis-like powers. Strong AI is highly integrated into the game as the artificial intelligence of the ship, Normandy, the race known as the Geth, and the main antagonists, the Reapers.
Deus Ex, a game published in 2000, depicts a dystopian society in the future where many current conspiracy theories such as Area 51 and FEMA makes up the plot of the game. In the game, players assume the role of a nanotechnically-augmented(nano-aug) agent. In the society, nano-augs are perceived to be far more adept than the average humanoid as their bodies have been physiologically augmented to perform super-human abilities. Although nano-agus are not considered machines, they suffer the stigma of not being formally human either. [18]
See Also
- Actor-Network Theory
- Artificial Intelligence and Technology
- Autonomous Systems
- Ghost in the Shell (series)
- "Human out of the Loop" Military Systems
- Mass Effect
- The Matrix
- Transhumanism
External Links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 “2045:The Year Man Becomes Immortal”, Lev Grossman, 10 February 2011, Time.com
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 Wikipedia: Technological singularity
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 “What is the Technological Singularity?”, Joel Falconer, 19 June 2011, thenextweb.com
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 “The Coming Technological Singularity: How to Survive in the Post-Human Era”, Vernor Vinge,1993.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 “The Singularity is Near”, Ray Kurzweil, the Penguin Group, 2005, pg. 21, 156, 178, 180, 182, 196, 202, 208, 215, 221, 250, 275, 287-296
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Wikipedia: Ray Kurzweil
- ↑ Wikipedia: Singularity University
- ↑ The Law of Accelerating Returns, kurzweilai.net
- ↑ Wikipedia: Accelerating change
- ↑ Wikipedia: Superintelligence
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "DEUS EX: Human Evolution?", Ed Moorhouse, 13 july 2011 whatculture.com
- ↑ Wikipedia: Ghost in the Shell
- ↑ The Prototype, 2013, Launchgram.com
- ↑ Wikipedia: I, Robot
- ↑ IMDB: The Maxtrix
- ↑ Player Starts Poll Asking BioWare for New Mass Effect 3 Ending [UPDATED], Phil Hornshaw, 9 March 2012, gamefront.com
- ↑ IMDB: Transcendent Man
- ↑ http://beefjack.com/features/human-revolution-vs-human-reality-the-science-of-deus-ex/