Non-fungible tokens

Non-fungible tokens, more commonly known as NFTs, are cryptographic tokens on a blockchain with unique identification codes and metadata. They let people tokenize things like art collectibles, and real estate. They can only have one official owner at a time and because they are stored on the blockchain their record of ownership can’t be altered.[2] Non-fungible is an economic term that is used to describe things that are not interchangeable for other items because they have unique properties. Fungible items however, can be exchanged for one another because they do not have unique properties.[2] Unlike cryptocurrencies, which are fungible tokens, they can’t be traded or exchanged at equal value because each is unique. [3] It is impossible for one non-fungible token to be equal to another because each token is unique due to their metadata. NFTs can be used to represent real world items like artwork, real estate, and clothing.[3]
Because NFTs exist on blockchains, they can be used to connect artists directly to their audiences, removing intermediaries and simplifying transactions.
Contents
Technology
Blockchains
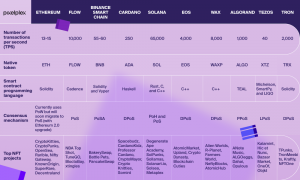
Some blockchains that support NFTs are Ethereum, Flow, Binance Smart Chain, Cardano, Solana, Algorand, Tezos, Tron and EOS. [5] Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for NFTs and has two popular token standards, ERC-721 (used for the creation of non-fungible tokens) and ERC-1155 (used for the creation of new semi-fungible tokens) To implement smart contracts, Ethereum makes use of Solidity, an object-oriented programming language created by the Ethereum team and compiled by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). The blockchain also features its own crypto called Ether (or ETH).[5] The Ethereum transaction fee varies based on network congestion and is usually between $100 and $200 per transaction, which is rather high compared to other blockchains.
IPFS
NFT Marketplaces
Opensea
Nifty Gateway
Looksrare
Rarible
Solsea
Foundation
Oneof
FTX
Coinbase
Superrare
Known Origin
Uses of NFTs
Fashion
Games
POAPs
Music
Art
Membership
Notable Examples
World of Women
Cryptopunks
Bored Ape Yacht Club
RTFKT Studios
Ethical Issues
Royalties
Climate
Artist payments
IP rights
References
- ↑ M. (2020, October 29). NFT Ecosystem Overview. The Nifty Crypto Nomad. https://niftycryptonomad.com/nft-ecosystem-overview/
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ethereum. (2022). Non-fungible tokens (NFT). Ethereum.Org. https://ethereum.org/en/nft/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Non-Fungible Token (NFT). (2021, December 14). Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/non-fungible-tokens-nft-5115211
- ↑ Team, P. (2022, January 25). Top Ten Blockchains Used in NFT Development. PixelPlex. https://pixelplex.io/blog/top-ten-blockchains-for-nft-development/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Team, P. (2022b, January 25). Top Ten Blockchains Used in NFT Development. PixelPlex. https://pixelplex.io/blog/top-ten-blockchains-for-nft-development/