Difference between revisions of "Hinge"
(→Privacy) |
m |
||
| (55 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Hinge is a location-based mobile dating application | + | [[File:deleted.png|400 px|thumbnail|right| Hinge advertisements promoting its "Designed to be Deleted" concept. <ref> O'Brien, Kyle. “Creative Director’s Choice: Madwell’s Chris Sojka on Hinge’s ‘Designed to be Deleted’ concept.” The Drum, The Drum, 12 Sept. 2019, https://www.thedrum.com/news/2019/09/12/creative-director-s-choice-madwell-s-chris-sojka-hinge-s-designed-be-deleted-concept. </ref> ]] |
| − | </ref> Hinge | + | |
| − | </ref> | + | Hinge is a location-based mobile dating application that utilizes what is known as a freemium model. <ref name = one>McAlone, Nathan. “Dating App Hinge Is Rolling Back Part of Its Big Reboot after Less than a Month.” Business Insider, Business Insider, 3 Nov. 2016, www.businessinsider.com/hinge-dating-app-moving-to-a-freemium-model-2016-11. Accessed 26 Mar. 2021.</ref> This model enables one to scroll through the profiles of other users and send someone else a ‘like’ to let them know that they would like to ‘match’ with them. <ref name = one/> Hinge has coined itself as “the relationship app” <ref name="Dale"> Markowitz, Dale. “Hinge's CEO Says a Good Dating App Relies on Vulnerability, Not Algorithms.” The Washington Post, WP Company, 31 Mar. 2019, www.washingtonpost.com/news/soloish/wp/2017/09/29/hinges-ceo-says-vulnerability-not-an-algorithm-is-the-key-to-a-good-dating-app/. </ref> and has advertised itself as an application that is “designed to be deleted.” <ref name="design"> Hinge. “8 Ways We Are Designed to Be Deleted.” Hinge, hinge.co/designed-to-be-deleted. </ref> According to Hinge, there are eight design elements within their application that are specifically intended to help foster genuine connections between users; these elements include requiring users' profiles to contain the answers to three personality-highlighting prompts, encouraging users to share their religious and political affiliations, and allowing free users to only send ten likes per day. <ref name="design" /> Asking users to share personal information, such as their political views, religious beliefs, and education history, is meant to help users find good matches and form better connections with others. However, sharing this much personal information comes at a cost; if users post personal and possibly sensitive information, that information can be made available to others in the event of a privacy breach. <ref name="delete"> Andrews, Frank. “Five Reasons You Should Delete Hinge.” VICE, 23 Nov. 2020, www.vice.com/en/article/n7vzbm/five-reasons-you-should-delete-hinge.</ref> |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | In September 2015, Vanity Fair published “Tinder and the Dawn of the Dating Apocalypse” | + | In 2012, Hinge was founded by CEO Justin McLeod. <ref>Shontell, Alyson. “A Dying Dating App Blew Its Last $25,000 On A Hail Mary - Now It's On Fire, Giving Tinder A Run For Its Money.” Business Insider, Business Insider, 22 Oct. 2014, www.businessinsider.com/meet-hinge-and-its-founder-justin-mcleod-2014-10. </ref> The dating application has since gone through several versions and revisions to become what it is today. <ref name="Dale" /> Originally, Hinge's model was similar to Tinder’s in that users swiped through profiles to seek matches. <ref name="Dale" /> To set themselves apart from other dating applications, Hinge's original design only matched users with friends of friends on Facebook. <ref name="Flynn"> Flynn, Kerry. “Dating App Hinge Relaunches, Making Serious Moves Away from Tinder.” Mashable, Mashable, 11 Oct. 2016, mashable.com/2016/10/11/hinge-relaunch/. </ref> |
| − | </ref> McLeod claimed that this article motivated him and his twenty-person team to rethink their approach and | + | |
| + | In September 2015, Vanity Fair published an article entitled “Tinder and the Dawn of the Dating Apocalypse” that went viral for its criticism of dating apps for creating a toxic hookup culture devoid of love and romance. <ref> Sales, Nancy Jo, and Photography by Justin Bishop. “Tinder and the Dawn of the Dating Apocalypse.” Vanity Fair, 2015, www.vanityfair.com/culture/2015/08/tinder-hook-up-culture-end-of-dating. </ref> McLeod claimed that this article motivated him and his twenty-person team to rethink their approach and build a dating app that aimed to do things differently. <ref name="Flynn" /> | ||
===Redesign=== | ===Redesign=== | ||
| + | |||
[[File:HINGE.png|thumbnail|right|Dating app matrix.<ref name="Flynn" />]] | [[File:HINGE.png|thumbnail|right|Dating app matrix.<ref name="Flynn" />]] | ||
| − | In January 2016, Hinge conducted user research | + | |
| + | In January 2016, Hinge conducted user research to gain a better understanding of what their audience wanted out of a dating app. <ref name="Flynn" /> Hinge's user research included a survey, the results of which revealed that users already found Hinge to be more relationship-leaning than other apps like Tinder. <ref name="Flynn" /> However, 70% of the survey's participants indicated that they’d like a dating app more serious than Hinge. <ref name="Flynn" /> At the time, only one in 500 Hinge swipes led to users exchanging phone numbers, and 81% of users claimed they had never found a long-term relationship on an app that utilized swiping. <ref name="mixpanel">Gillespie, Christopher. “Giving up the Ghost: How Hinge Disrupted Online Dating with Data and Helped Users Find Love.” Mixpanel, The Signal, 24 July 2020, mixpanel.com/blog/how-hinge-disrupted-online-dating-2/.</ref> | ||
| − | Later in 2016, Hinge | + | Later in 2016, Hinge entirely redesigned their application; they moved away from the traditional ‘swiping’ model and created a new design that allowed users to scroll through other user’s profiles. <ref name="Flynn" /> These changes also included removing expirations on matches <ref name="Flynn" /> and charging users $7 a month in an attempt to weed out non-serious users. <ref name="Anna"> Iovine, Anna. “Hinge's Founder Leans into Data to Set the Dating App Apart from the Pack.” Mashable, Mashable, 2 Dec. 2019, mashable.com/article/hinge-justin-mcleod-interview/.</ref> Hinge's new model created connections that led to full-on conversations five times more than the previous version, and users exchanged phone numbers seven times as often as before. <ref name="Flynn" /> By 2017, Hinge had reverted back to a freemium model. <ref name="Anna" /> |
| − | === | + | ===Present=== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic forced many traditional social outlets, such as bars and restaurants, to close for extended periods of time. This led to a significant spike in dating app usage, resulting in Hinge tripling its revenue and an 82% growth in downloads of the application. <ref> Schafer, Brett. “Could Hinge Be Match Group's Next Tinder?” The Motley Fool, The Motley Fool, 10 Nov. 2020, www.fool.com/investing/2020/11/10/could-hinge-be-match-groups-next-tinder/?source=aw&awc=21748_1615490421_90612bb0a82ad3715e0b0b9484b1e0e7. </ref> The application also facilitated 12% more dates in 2020 than it did in 2019. <ref> Robinson, E. (16 March 2021). Dating app ‘Hinge’ sees increase in video dates during pandemic. Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.kxly.com/dating-app-hinge-sees-increase-in-video-dates-during-pandemic/ </ref> The pandemic also resulted in an increase in video dates. As a result of this, hinge decided to integrate conversation prompts into its video chatting feature. Retrieved 15 April 2021, from https://www.adweek.com/performance-marketing/hinge-levels-up-virtual-dating-with-launch-of-video-prompts/ </ref> | |
| − | === | + | Additionally, Hinge has partnered with Uncommon Goods, a gifting e-tailer, to promote virtual dating during the pandemic with cocktail kits that include ice-breaking conversation starters. <ref> Cornish, K. (18 March 2021). "Hinge Partnered With Uncommon Goods To Create the Perfect Virtual Date Night Kit". Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.travelandleisure.com/style/shopping/hinge-uncommon-goods-virtual-date-kit </ref> |
| − | In addition to Tinder and Bumble, | + | |
| + | ===Competition=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:thursday.png|400 px|thumbnail|right| One of Thursday's advertisements promoting the idea that the application opens for one day a week. <ref> Ward, Amelia. “New Dating App Thursday Only Works For One Day Of The Week.” Lad Bible, Lad Bible Group, 1 Dec. 2020, https://www.ladbible.com/news/interesting-unilever-plans-tests-of-four-day-week-for-all-new-zealand-staff-20201201. </ref> ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to popular dating applications like Tinder and Bumble, the new dating application Thursday aims to switch up the rules typically followed by online dating applications. <ref name="thurs"> Forsey, Z. (15 March 2021). Thursday, the new dating app taking on Hinge and Tinder by changing all the rules. Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.mirror.co.uk/tech/thursday-new-dating-app-taking-23688333 </ref> Thursday's model is based on the idea that their app only works one day a week. <ref name="thurs" /> On that day, users are encouraged to go on the app in the morning only if they are free that same night. <ref name="thurs" /> This is because all matches and conversations disappear at midnight on the day the app is active, so users have to act quickly if they want to find someone. <ref name="thurs" /> The model's design aims to reduce small talk by encouraging users to meet on the same day they match with each other. <ref name="thurs" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tinder has begun collaboration with Lyft so that users can book rides to and from dates without having to leave Tinder's app. <ref> Campbell, Ian Carlos. “Tinder Will Soon Let You Gift a Lyft Ride to Your Date.” The Verge, The Verge, 22 Mar. 2021, https://theverge.com/2021/3/22/22345181/tinder-lyft-gift-ride-date.</ref> With this feature, users will also be able to gift rides to their dates directly through the Tinder app. <ref>“Tinder Will Let Users Gift Lyft Rides to Their Dates through a New Partnership.” Yahoo! News, Yahoo!, https://news.yahoo.com/tinder-let-users-gift-lyft-163935858.html.</ref> Tinder's plan is to roll this feature out in the upcoming months as in-person dates become safer. Tinder is also planning to introduce in-app background checks, which could be potentially groundbreaking for user privacy and safety. The in-app background checks will allow users to view public records about potential dates with a search involving the person's name or phone number. The background checks, however, will not include any details about traffic violations or drug charges. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tinder's parent company, Match Group, plans to eventually make this feature available across all of the platforms it owns, including Hinge, OkCupid, and PlentyOfFish. One of the reasons in-app background checks are being developed for dating applications is that members of the public are pushing for dating apps to take more responsibility for their users' safety. <ref>Godwin, Cody. “Tinder to Introduce in-App Background Checks.” BBC News, BBC, 15 Mar. 2021, https://bbc.com/news/technology-56409427.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===How Hinge is Used=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hinge can be utilized in a variety of different ways to help users find short-term relationships, long-term relationships, or hook-ups. According to Universe News Network, unlike applications like Tinder, Hinge is associated more with people who are looking for serious relationships. <ref>Bishop, Roger. The Cost of Finding Love Through Dating Apps. 4 Jan. 2021, https://universenewsnetwork.com/2021/04/01/the-cost-of-finding-love-through-dating-apps/.</ref> However, Jas Bagniewski, the cofounder of a couples’ sex therapy application, claims that "Hinge is where people go when you want to get laid." <ref>Isabel Woodford 29 March 2021, et al. “Can Relationship Tech Create the next Tinder?” Sifted, 29 Mar. 2021, https://sifted.eu/articles/startups-fixing-love-digitally/.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | While the application itself is free, users can pay for Hinge Preferred, an upgraded version of Hinge, for access to more exclusive features. The prices for Hinge Preferred are as follows: $19.99 for one month, $39.99 for three months, and $59.99 for six months. Those with Hinge Preferred can send unlimited likes to other users and see every user who likes them. Free users can only send ten likes a day and are only able to see those who has liked them if both users have liked each other. | ||
==Ethical Implications== | ==Ethical Implications== | ||
| + | |||
===Privacy=== | ===Privacy=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | Hinge | + | Hinge claims to use people's data to help them match with their ideal partner. <ref name="design"/> The company also has its own research team, HingeLabs, that is said to use behavioral data for the purpose of creating more successful interactions between users. <ref> “Hinge Labs.” Hingelabs.co, www.hingelabs.co/. </ref> In a 2019 interview, Justin McLeod noted that Hinge’s algorithm “gets better and more accurate the more that you reveal your tastes.” <ref> Maitland, Hayley. “The Founder Of Hinge Has Some Thoughts On Your Dating Profile.” British Vogue, British Vogue, 14 Aug. 2019, www.vogue.co.uk/article/justin-mcleod-hinge-founder-interview-2019. </ref> To help people find matches, Hinge encourages users to share a lot of personal information on the application; this includes educational background, occupation, age, and height. <ref name="delete" /> This information can get more sensitive if users choose to share their drug habits, location, and preferences (or ‘dealbreakers’) in a partner when it comes to religion or ethnicity. <ref name="delete" /> If this type of sensitive information got leaked, there could be detrimental consequences for Hinge's users. For instance, admitting to drug use on the application could cost someone their job, or information regarding someone’s sexual orientation could be used for blackmail. Hinge’s privacy policy states that “we do not promise, and you should not expect, that your personal information will always remain secure,” which could prove concerning for users. <ref name="Anna" /> Another implication of users posting personal information online is that this data could potentially be weaponized by foreign intelligence agencies. <ref name = "nbc">Ferguson, Conor, et al. “Dating Apps like Grindr Could Pose a National Security Risk, Experts Warn.” NBCNews.com, NBCUniversal News Group, 16 Jan. 2020, www.nbcnews.com/tech/security/dating-apps-grindr-could-pose-national-security-risk-experts-warn-n1115321.</ref> |
| − | </ref> | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Hinge | + | Hinge is owned by a company called Match Group, which has experienced security breaches in the past. In 2016, researchers found public information on 70,000 OKCupid users, and in 2020, more than 70,000 Tinder photos of women were shared online without users’ consent or knowledge. <ref> Zimmer, Michael. “OkCupid Study Reveals the Perils of Big-Data Science.” Wired, Conde Nast, 3 June 2017, www.wired.com/2016/05/okcupid-study-reveals-perils-big-data-science/. </ref> Additionally, Hinge's user data is accessible to all of the other 45 dating companies owned by Match Group. <ref name="delete" /> However, Match Group insists that they do not share users' personal data with third parties for advertising purposes. <ref name = "consumer">Germain, Thomas. “How Private Is Your Online Dating Data?” Consumer Reports, 21 Sept. 2019, www.consumerreports.org/privacy/how-private-is-your-online-dating-data/. </ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Hinge shares data with third party companies. <ref name="delete" /> More specifically, the application’s privacy preferences outline ten third-party marketing tools that enable companies to track users' activity on the internet. <ref name="delete" /> Currently, users can only opt out of two of these tools. <ref name="delete" /> Users can also request to view what data a dating application has collected on them from their profile. <ref name = "nbc"></ref> Because of European laws that require dating applications to turn over user data upon request, one user discovered that in her six months of using Hinge, the company had acquired 250 pages of information on her. <ref name = "nbc"></ref> However, in the US, there are currently no requirements for companies to provide this information. <ref name = "nbc"></ref> Users of dating applications have expressed concerns regarding their data being shared; reports show that users believe their data should only be available to them and the other users they interact with on the application. <ref name = "nbc"></ref> While there is no requirement in the US for companies to provide users access to their personal data, Hinge allows users to request a copy of this information. <ref name="hingeapp">“How Do I Request a Copy of My Personal Data?” Hinge, hingeapp.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360011235813-How-do-I-request-a-copy-of-my-personal-data-.</ref> Users can request a report of their personal data within the Hinge app, which becomes available less than 48 hours after the request is made <ref name="hingeapp" />. In the interest of people's privacy and security, the user will have access to their personal data for 48 hours before it expires. <ref name="hingeapp" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Online Dating and Trust=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Online dating, which includes the use of dating applications, “is not impervious to worrisome trust” raised by the “exposure to self-reported (and thus potentially misrepresented) information.” <ref> Norcie, Gregory, Emiliano De Cristofaro, and Victoria Bellotti. "Bootstrapping Trust in Online Dating: Social Verification of Online Dating Profiles." Financial Cryptography and Data Security, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41320-9_10. </ref> This misrepresented information may come in the form of users lying about their personal information, such as their age, height, and weight. <ref name = a> Stanier, James, et al. "Can We Use Trust in Online Dating?." Journal of Wireless Mobile Networks, Ubiquitous Computing, and Dependable Applications, 2010, https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/29833644/paper-tcdc2010_cwutiod.pdf?1351794726=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DCan_We_Use_Trust_in_Online_Dating.pdf&Expires=1618522670&Signature=BWKvmVWuR77KYy2oO14Uh~mjYjrhDdeV0YNucjDHBiyS~EcWtv6fgAyQsxk1XKI15MON4sRBMZwDcfzcWxlJ5lklmHfzS9yV~ZmEoGYL526hrIIRqdxkfAVpZXX1nNCAPR~-N~0uTwyUO1ZjOyJMMV0XN3pePiVY7SFdQCW7ymbgNQyM-IQ5QaHEggKSGCey45wGZ0Pdqrv~D-35PVLNT-sGwdZglFhb1KBTgd2HmiqfoFkjmckWQDMti9MemnRX~MMpKG5UHOZAQG3Gcd~CVPmaDjZKobf~3rFEvIaBtUwmeBpgw~WEtxaS0JgXuS7mI8hvnRUFHLKVt8OowCarfA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA. </ref> Those who participate in online dating might also pose in certain manners, edit their photos, or use outdated photos to maximize their perceived physical attractiveness. <ref> Ellison, N., Heino, R., & Gibbs, J. “Managing Impressions Online: Self-Presentation Processes in the Online Dating Environment.” Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 2006, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2006.00020.x. </ref> Roughly “a third of photographs” on online dating platforms “are rated as being ‘inaccurate’ in their depiction of the member.” <ref> Masden, C., & Edwards, W. K. (2015). “Understanding the Role of Community in Online Dating.” Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1145/2702123.2702417. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In accordance with the issue of misrepresented information and online dating, Hinge has recently coined the term “kittenfishing,” which “is like a lower-grade, less-egregious version of catfishing.” <ref name = b> Wong, Brittany. “If You’re Dating, You’ve Almost Undoubtedly Been Kittenfished.” The Huffington Post, BuzzFeed Inc., 11 Jul. 2018, https://www.huffpost.com/entry/dating-kittenfishing-catfishing_n_5b44f652e4b048036ea342fc. </ref> A kittenfisher often misrepresents themselves on their Hinge profile by “using heavily edited or old-as-hell pics, or by lying about their age or lifestyle to curry favor with their matches.” <ref name = b/> A survey conducted by Hinge found that “38 percent of men and 24 percent of women reported being kittenfished.” <ref> Tegtmeyer, Lauren. “The Lies We Tell On Dating Apps.” Bustle, Bustle, 30 Oct. 2020, https://www.bustle.com/life/the-lies-we-tell-on-dating-apps. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Users might also misrepresent information about themselves by lying about their relationship status and falsely claiming that they are single. <ref name = a/> The results of “a large nationally representative study in the Netherlands” revealed that “4% of male participants and 2% of female participants admitted using an online dating website or mobile dating app while being in a committed relationship.” <ref> Timmermans, Elisabeth, Elien De Caluwé, and Cassandra Alexopoulos. "Why Are You Cheating on Tinder? Exploring Users' Motives and (dark) Personality Traits." Computers in Human Behavior, Dec. 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.07.040. </ref> In 2015, Hinge researched its users and found that 3.6% of them were “married, engaged, or in a relationship.” <ref name = c> Kelly, Heather. “Dating app Hinge cracks down on cheaters.” CNN Business, Cable News Network, 15 May 2015, https://money.cnn.com/2015/05/14/technology/hinge-relationship-status/index.html. </ref> In comparison, a “study of Tinder users by Globalwebindex found that 42% of people on that service were in a relationship or married.” <ref name = c/> However, to ensure that “Hinge remains a trusted place for finding relationships,” the company introduced a feature on their application that would automatically add “users' Facebook relationship status to their profiles.” <ref name = c/> | ||
===Hinge can share user data with police=== | ===Hinge can share user data with police=== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | According to Hinge’s Privacy Policy, users agree that under necessary circumstances, user data can be shared with the police. <ref name="privacy"> Hinge. “Privacy.” Hinge, hinge.co/privacy.html. </ref> Admitting to illegal actions on Hinge, such as underage drinking or recreational drug use, could be cause for legal action. | ||
===Lawsuit Against Hinge=== | ===Lawsuit Against Hinge=== | ||
| − | In 2021, a visually-impaired Brooklyn woman | + | |
| + | In 2021, Aretha Crosson, a visually-impaired Brooklyn woman, sued Hinge. <ref name="lawsuit"> Goldberg, N. (19 March 2021). NYC blind woman sues Hinge in federal court, says she can’t use dating app, Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.nydailynews.com/new-york/ny-blind-woman-sues-hinge-app-not-accessible-dating-20210319-p5rh7gxwlbe75ac3th6dpnqoni-story.html </ref>. She argued that Hinge's interface is inaccessible to blind individuals, ostracizing these people from the opportunities that online dating offers. <ref name="lawsuit"/> Crosson claimed that she wanted to utilize Hinge to help her make friends and possibly find love, but due to the application's design, it was virtually impossible for her to do so. <ref name="lawsuit" /> She contended that Hinge's application violates the Americans with Disabilities Act, as it fails to provide equal access to those with disabilities. <ref name="lawsuit" /> In total, Crosson has sued 77 different companies in Brooklyn Federal Court over similar issues. <ref name="lawsuit" /> Hinge did not immediately respond to a request for a comment on the suit. <ref name="lawsuit" /> | ||
===Using Hinge data to derail sexual assault cases=== | ===Using Hinge data to derail sexual assault cases=== | ||
| − | Hinge | + | |
| + | Hinge keeps all of its users’ messaging history, and these records can be used against them. Multiple women have come forward and reported that they were raped or attacked on a date that came from a dating application, and in some cases, the courts have used these women's messaging history against them to show that they were flirting or arranging to meet with the alleged perpetrator. <ref name="delete" /> | ||
===Hinge can keep user data forever=== | ===Hinge can keep user data forever=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Hinge’s privacy policy states that they can keep users' personal data forever, even for accounts that have been deleted. <ref name="privacy" /> | |
| − | + | ||
[[File:hingeapp.jpg|thumbnail|right|Hinge app interface. <ref name="hannah" />]] | [[File:hingeapp.jpg|thumbnail|right|Hinge app interface. <ref name="hannah" />]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Enabling users to discriminate by ethnicity and religion=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In line with other dating applications, Hinge allows its users to set preferences for the age range and their distance from other users. Additionally, Hinge's premium members have access to a feature that allows them to filter who pops up on their feed based on height, ethnicity, and religion. <ref name="hannah"> Smothers, Hannah. “This Controversial New Dating App Feature Allows You to Choose Which Ethnicities You See.” Cosmopolitan, Cosmopolitan, 9 Oct. 2017, www.cosmopolitan.com/sex-love/a7204682/hinge-ethnicity-preference/.</ref> Those with access to this feature can list certain heights, ethnicities, and races as preferences or ‘dealbreakers’ and will then be shown other users that fit their criteria. <ref name="hannah" /> This feature has proved controversial and had been criticized for enabling racism on the app. <ref name="hannah" /> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 15 April 2021

Hinge is a location-based mobile dating application that utilizes what is known as a freemium model. [2] This model enables one to scroll through the profiles of other users and send someone else a ‘like’ to let them know that they would like to ‘match’ with them. [2] Hinge has coined itself as “the relationship app” [3] and has advertised itself as an application that is “designed to be deleted.” [4] According to Hinge, there are eight design elements within their application that are specifically intended to help foster genuine connections between users; these elements include requiring users' profiles to contain the answers to three personality-highlighting prompts, encouraging users to share their religious and political affiliations, and allowing free users to only send ten likes per day. [4] Asking users to share personal information, such as their political views, religious beliefs, and education history, is meant to help users find good matches and form better connections with others. However, sharing this much personal information comes at a cost; if users post personal and possibly sensitive information, that information can be made available to others in the event of a privacy breach. [5]
Contents
History
In 2012, Hinge was founded by CEO Justin McLeod. [6] The dating application has since gone through several versions and revisions to become what it is today. [3] Originally, Hinge's model was similar to Tinder’s in that users swiped through profiles to seek matches. [3] To set themselves apart from other dating applications, Hinge's original design only matched users with friends of friends on Facebook. [7]
In September 2015, Vanity Fair published an article entitled “Tinder and the Dawn of the Dating Apocalypse” that went viral for its criticism of dating apps for creating a toxic hookup culture devoid of love and romance. [8] McLeod claimed that this article motivated him and his twenty-person team to rethink their approach and build a dating app that aimed to do things differently. [7]
Redesign
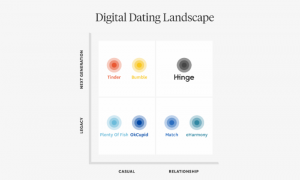
In January 2016, Hinge conducted user research to gain a better understanding of what their audience wanted out of a dating app. [7] Hinge's user research included a survey, the results of which revealed that users already found Hinge to be more relationship-leaning than other apps like Tinder. [7] However, 70% of the survey's participants indicated that they’d like a dating app more serious than Hinge. [7] At the time, only one in 500 Hinge swipes led to users exchanging phone numbers, and 81% of users claimed they had never found a long-term relationship on an app that utilized swiping. [9]
Later in 2016, Hinge entirely redesigned their application; they moved away from the traditional ‘swiping’ model and created a new design that allowed users to scroll through other user’s profiles. [7] These changes also included removing expirations on matches [7] and charging users $7 a month in an attempt to weed out non-serious users. [10] Hinge's new model created connections that led to full-on conversations five times more than the previous version, and users exchanged phone numbers seven times as often as before. [7] By 2017, Hinge had reverted back to a freemium model. [10]
Present
In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic forced many traditional social outlets, such as bars and restaurants, to close for extended periods of time. This led to a significant spike in dating app usage, resulting in Hinge tripling its revenue and an 82% growth in downloads of the application. [11] The application also facilitated 12% more dates in 2020 than it did in 2019. [12] The pandemic also resulted in an increase in video dates. As a result of this, hinge decided to integrate conversation prompts into its video chatting feature. Retrieved 15 April 2021, from https://www.adweek.com/performance-marketing/hinge-levels-up-virtual-dating-with-launch-of-video-prompts/ </ref>
Additionally, Hinge has partnered with Uncommon Goods, a gifting e-tailer, to promote virtual dating during the pandemic with cocktail kits that include ice-breaking conversation starters. [13]
Competition
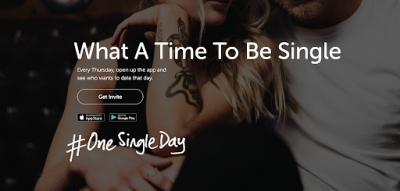
In addition to popular dating applications like Tinder and Bumble, the new dating application Thursday aims to switch up the rules typically followed by online dating applications. [15] Thursday's model is based on the idea that their app only works one day a week. [15] On that day, users are encouraged to go on the app in the morning only if they are free that same night. [15] This is because all matches and conversations disappear at midnight on the day the app is active, so users have to act quickly if they want to find someone. [15] The model's design aims to reduce small talk by encouraging users to meet on the same day they match with each other. [15]
Tinder has begun collaboration with Lyft so that users can book rides to and from dates without having to leave Tinder's app. [16] With this feature, users will also be able to gift rides to their dates directly through the Tinder app. [17] Tinder's plan is to roll this feature out in the upcoming months as in-person dates become safer. Tinder is also planning to introduce in-app background checks, which could be potentially groundbreaking for user privacy and safety. The in-app background checks will allow users to view public records about potential dates with a search involving the person's name or phone number. The background checks, however, will not include any details about traffic violations or drug charges.
Tinder's parent company, Match Group, plans to eventually make this feature available across all of the platforms it owns, including Hinge, OkCupid, and PlentyOfFish. One of the reasons in-app background checks are being developed for dating applications is that members of the public are pushing for dating apps to take more responsibility for their users' safety. [18]
How Hinge is Used
Hinge can be utilized in a variety of different ways to help users find short-term relationships, long-term relationships, or hook-ups. According to Universe News Network, unlike applications like Tinder, Hinge is associated more with people who are looking for serious relationships. [19] However, Jas Bagniewski, the cofounder of a couples’ sex therapy application, claims that "Hinge is where people go when you want to get laid." [20]
While the application itself is free, users can pay for Hinge Preferred, an upgraded version of Hinge, for access to more exclusive features. The prices for Hinge Preferred are as follows: $19.99 for one month, $39.99 for three months, and $59.99 for six months. Those with Hinge Preferred can send unlimited likes to other users and see every user who likes them. Free users can only send ten likes a day and are only able to see those who has liked them if both users have liked each other.
Ethical Implications
Privacy
Hinge claims to use people's data to help them match with their ideal partner. [4] The company also has its own research team, HingeLabs, that is said to use behavioral data for the purpose of creating more successful interactions between users. [21] In a 2019 interview, Justin McLeod noted that Hinge’s algorithm “gets better and more accurate the more that you reveal your tastes.” [22] To help people find matches, Hinge encourages users to share a lot of personal information on the application; this includes educational background, occupation, age, and height. [5] This information can get more sensitive if users choose to share their drug habits, location, and preferences (or ‘dealbreakers’) in a partner when it comes to religion or ethnicity. [5] If this type of sensitive information got leaked, there could be detrimental consequences for Hinge's users. For instance, admitting to drug use on the application could cost someone their job, or information regarding someone’s sexual orientation could be used for blackmail. Hinge’s privacy policy states that “we do not promise, and you should not expect, that your personal information will always remain secure,” which could prove concerning for users. [10] Another implication of users posting personal information online is that this data could potentially be weaponized by foreign intelligence agencies. [23]
Hinge is owned by a company called Match Group, which has experienced security breaches in the past. In 2016, researchers found public information on 70,000 OKCupid users, and in 2020, more than 70,000 Tinder photos of women were shared online without users’ consent or knowledge. [24] Additionally, Hinge's user data is accessible to all of the other 45 dating companies owned by Match Group. [5] However, Match Group insists that they do not share users' personal data with third parties for advertising purposes. [25]
Hinge shares data with third party companies. [5] More specifically, the application’s privacy preferences outline ten third-party marketing tools that enable companies to track users' activity on the internet. [5] Currently, users can only opt out of two of these tools. [5] Users can also request to view what data a dating application has collected on them from their profile. [23] Because of European laws that require dating applications to turn over user data upon request, one user discovered that in her six months of using Hinge, the company had acquired 250 pages of information on her. [23] However, in the US, there are currently no requirements for companies to provide this information. [23] Users of dating applications have expressed concerns regarding their data being shared; reports show that users believe their data should only be available to them and the other users they interact with on the application. [23] While there is no requirement in the US for companies to provide users access to their personal data, Hinge allows users to request a copy of this information. [26] Users can request a report of their personal data within the Hinge app, which becomes available less than 48 hours after the request is made [26]. In the interest of people's privacy and security, the user will have access to their personal data for 48 hours before it expires. [26]
Online Dating and Trust
Online dating, which includes the use of dating applications, “is not impervious to worrisome trust” raised by the “exposure to self-reported (and thus potentially misrepresented) information.” [27] This misrepresented information may come in the form of users lying about their personal information, such as their age, height, and weight. [28] Those who participate in online dating might also pose in certain manners, edit their photos, or use outdated photos to maximize their perceived physical attractiveness. [29] Roughly “a third of photographs” on online dating platforms “are rated as being ‘inaccurate’ in their depiction of the member.” [30]
In accordance with the issue of misrepresented information and online dating, Hinge has recently coined the term “kittenfishing,” which “is like a lower-grade, less-egregious version of catfishing.” [31] A kittenfisher often misrepresents themselves on their Hinge profile by “using heavily edited or old-as-hell pics, or by lying about their age or lifestyle to curry favor with their matches.” [31] A survey conducted by Hinge found that “38 percent of men and 24 percent of women reported being kittenfished.” [32]
Users might also misrepresent information about themselves by lying about their relationship status and falsely claiming that they are single. [28] The results of “a large nationally representative study in the Netherlands” revealed that “4% of male participants and 2% of female participants admitted using an online dating website or mobile dating app while being in a committed relationship.” [33] In 2015, Hinge researched its users and found that 3.6% of them were “married, engaged, or in a relationship.” [34] In comparison, a “study of Tinder users by Globalwebindex found that 42% of people on that service were in a relationship or married.” [34] However, to ensure that “Hinge remains a trusted place for finding relationships,” the company introduced a feature on their application that would automatically add “users' Facebook relationship status to their profiles.” [34]
According to Hinge’s Privacy Policy, users agree that under necessary circumstances, user data can be shared with the police. [35] Admitting to illegal actions on Hinge, such as underage drinking or recreational drug use, could be cause for legal action.
Lawsuit Against Hinge
In 2021, Aretha Crosson, a visually-impaired Brooklyn woman, sued Hinge. [36]. She argued that Hinge's interface is inaccessible to blind individuals, ostracizing these people from the opportunities that online dating offers. [36] Crosson claimed that she wanted to utilize Hinge to help her make friends and possibly find love, but due to the application's design, it was virtually impossible for her to do so. [36] She contended that Hinge's application violates the Americans with Disabilities Act, as it fails to provide equal access to those with disabilities. [36] In total, Crosson has sued 77 different companies in Brooklyn Federal Court over similar issues. [36] Hinge did not immediately respond to a request for a comment on the suit. [36]
Using Hinge data to derail sexual assault cases
Hinge keeps all of its users’ messaging history, and these records can be used against them. Multiple women have come forward and reported that they were raped or attacked on a date that came from a dating application, and in some cases, the courts have used these women's messaging history against them to show that they were flirting or arranging to meet with the alleged perpetrator. [5]
Hinge can keep user data forever
Hinge’s privacy policy states that they can keep users' personal data forever, even for accounts that have been deleted. [35]
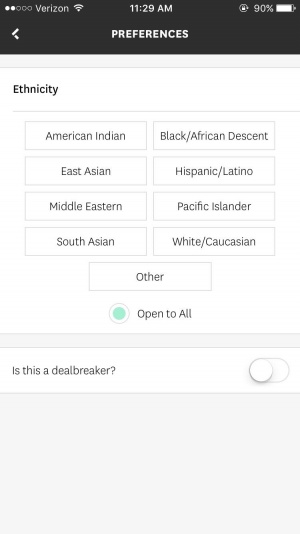
Enabling users to discriminate by ethnicity and religion
In line with other dating applications, Hinge allows its users to set preferences for the age range and their distance from other users. Additionally, Hinge's premium members have access to a feature that allows them to filter who pops up on their feed based on height, ethnicity, and religion. [37] Those with access to this feature can list certain heights, ethnicities, and races as preferences or ‘dealbreakers’ and will then be shown other users that fit their criteria. [37] This feature has proved controversial and had been criticized for enabling racism on the app. [37]
References
- ↑ O'Brien, Kyle. “Creative Director’s Choice: Madwell’s Chris Sojka on Hinge’s ‘Designed to be Deleted’ concept.” The Drum, The Drum, 12 Sept. 2019, https://www.thedrum.com/news/2019/09/12/creative-director-s-choice-madwell-s-chris-sojka-hinge-s-designed-be-deleted-concept.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 McAlone, Nathan. “Dating App Hinge Is Rolling Back Part of Its Big Reboot after Less than a Month.” Business Insider, Business Insider, 3 Nov. 2016, www.businessinsider.com/hinge-dating-app-moving-to-a-freemium-model-2016-11. Accessed 26 Mar. 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Markowitz, Dale. “Hinge's CEO Says a Good Dating App Relies on Vulnerability, Not Algorithms.” The Washington Post, WP Company, 31 Mar. 2019, www.washingtonpost.com/news/soloish/wp/2017/09/29/hinges-ceo-says-vulnerability-not-an-algorithm-is-the-key-to-a-good-dating-app/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Hinge. “8 Ways We Are Designed to Be Deleted.” Hinge, hinge.co/designed-to-be-deleted.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Andrews, Frank. “Five Reasons You Should Delete Hinge.” VICE, 23 Nov. 2020, www.vice.com/en/article/n7vzbm/five-reasons-you-should-delete-hinge.
- ↑ Shontell, Alyson. “A Dying Dating App Blew Its Last $25,000 On A Hail Mary - Now It's On Fire, Giving Tinder A Run For Its Money.” Business Insider, Business Insider, 22 Oct. 2014, www.businessinsider.com/meet-hinge-and-its-founder-justin-mcleod-2014-10.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 Flynn, Kerry. “Dating App Hinge Relaunches, Making Serious Moves Away from Tinder.” Mashable, Mashable, 11 Oct. 2016, mashable.com/2016/10/11/hinge-relaunch/.
- ↑ Sales, Nancy Jo, and Photography by Justin Bishop. “Tinder and the Dawn of the Dating Apocalypse.” Vanity Fair, 2015, www.vanityfair.com/culture/2015/08/tinder-hook-up-culture-end-of-dating.
- ↑ Gillespie, Christopher. “Giving up the Ghost: How Hinge Disrupted Online Dating with Data and Helped Users Find Love.” Mixpanel, The Signal, 24 July 2020, mixpanel.com/blog/how-hinge-disrupted-online-dating-2/.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Iovine, Anna. “Hinge's Founder Leans into Data to Set the Dating App Apart from the Pack.” Mashable, Mashable, 2 Dec. 2019, mashable.com/article/hinge-justin-mcleod-interview/.
- ↑ Schafer, Brett. “Could Hinge Be Match Group's Next Tinder?” The Motley Fool, The Motley Fool, 10 Nov. 2020, www.fool.com/investing/2020/11/10/could-hinge-be-match-groups-next-tinder/?source=aw&awc=21748_1615490421_90612bb0a82ad3715e0b0b9484b1e0e7.
- ↑ Robinson, E. (16 March 2021). Dating app ‘Hinge’ sees increase in video dates during pandemic. Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.kxly.com/dating-app-hinge-sees-increase-in-video-dates-during-pandemic/
- ↑ Cornish, K. (18 March 2021). "Hinge Partnered With Uncommon Goods To Create the Perfect Virtual Date Night Kit". Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.travelandleisure.com/style/shopping/hinge-uncommon-goods-virtual-date-kit
- ↑ Ward, Amelia. “New Dating App Thursday Only Works For One Day Of The Week.” Lad Bible, Lad Bible Group, 1 Dec. 2020, https://www.ladbible.com/news/interesting-unilever-plans-tests-of-four-day-week-for-all-new-zealand-staff-20201201.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 Forsey, Z. (15 March 2021). Thursday, the new dating app taking on Hinge and Tinder by changing all the rules. Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.mirror.co.uk/tech/thursday-new-dating-app-taking-23688333
- ↑ Campbell, Ian Carlos. “Tinder Will Soon Let You Gift a Lyft Ride to Your Date.” The Verge, The Verge, 22 Mar. 2021, https://theverge.com/2021/3/22/22345181/tinder-lyft-gift-ride-date.
- ↑ “Tinder Will Let Users Gift Lyft Rides to Their Dates through a New Partnership.” Yahoo! News, Yahoo!, https://news.yahoo.com/tinder-let-users-gift-lyft-163935858.html.
- ↑ Godwin, Cody. “Tinder to Introduce in-App Background Checks.” BBC News, BBC, 15 Mar. 2021, https://bbc.com/news/technology-56409427.
- ↑ Bishop, Roger. The Cost of Finding Love Through Dating Apps. 4 Jan. 2021, https://universenewsnetwork.com/2021/04/01/the-cost-of-finding-love-through-dating-apps/.
- ↑ Isabel Woodford 29 March 2021, et al. “Can Relationship Tech Create the next Tinder?” Sifted, 29 Mar. 2021, https://sifted.eu/articles/startups-fixing-love-digitally/.
- ↑ “Hinge Labs.” Hingelabs.co, www.hingelabs.co/.
- ↑ Maitland, Hayley. “The Founder Of Hinge Has Some Thoughts On Your Dating Profile.” British Vogue, British Vogue, 14 Aug. 2019, www.vogue.co.uk/article/justin-mcleod-hinge-founder-interview-2019.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 23.4 Ferguson, Conor, et al. “Dating Apps like Grindr Could Pose a National Security Risk, Experts Warn.” NBCNews.com, NBCUniversal News Group, 16 Jan. 2020, www.nbcnews.com/tech/security/dating-apps-grindr-could-pose-national-security-risk-experts-warn-n1115321.
- ↑ Zimmer, Michael. “OkCupid Study Reveals the Perils of Big-Data Science.” Wired, Conde Nast, 3 June 2017, www.wired.com/2016/05/okcupid-study-reveals-perils-big-data-science/.
- ↑ Germain, Thomas. “How Private Is Your Online Dating Data?” Consumer Reports, 21 Sept. 2019, www.consumerreports.org/privacy/how-private-is-your-online-dating-data/.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 “How Do I Request a Copy of My Personal Data?” Hinge, hingeapp.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360011235813-How-do-I-request-a-copy-of-my-personal-data-.
- ↑ Norcie, Gregory, Emiliano De Cristofaro, and Victoria Bellotti. "Bootstrapping Trust in Online Dating: Social Verification of Online Dating Profiles." Financial Cryptography and Data Security, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41320-9_10.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Stanier, James, et al. "Can We Use Trust in Online Dating?." Journal of Wireless Mobile Networks, Ubiquitous Computing, and Dependable Applications, 2010, https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/29833644/paper-tcdc2010_cwutiod.pdf?1351794726=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DCan_We_Use_Trust_in_Online_Dating.pdf&Expires=1618522670&Signature=BWKvmVWuR77KYy2oO14Uh~mjYjrhDdeV0YNucjDHBiyS~EcWtv6fgAyQsxk1XKI15MON4sRBMZwDcfzcWxlJ5lklmHfzS9yV~ZmEoGYL526hrIIRqdxkfAVpZXX1nNCAPR~-N~0uTwyUO1ZjOyJMMV0XN3pePiVY7SFdQCW7ymbgNQyM-IQ5QaHEggKSGCey45wGZ0Pdqrv~D-35PVLNT-sGwdZglFhb1KBTgd2HmiqfoFkjmckWQDMti9MemnRX~MMpKG5UHOZAQG3Gcd~CVPmaDjZKobf~3rFEvIaBtUwmeBpgw~WEtxaS0JgXuS7mI8hvnRUFHLKVt8OowCarfA__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA.
- ↑ Ellison, N., Heino, R., & Gibbs, J. “Managing Impressions Online: Self-Presentation Processes in the Online Dating Environment.” Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 2006, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2006.00020.x.
- ↑ Masden, C., & Edwards, W. K. (2015). “Understanding the Role of Community in Online Dating.” Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1145/2702123.2702417.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 Wong, Brittany. “If You’re Dating, You’ve Almost Undoubtedly Been Kittenfished.” The Huffington Post, BuzzFeed Inc., 11 Jul. 2018, https://www.huffpost.com/entry/dating-kittenfishing-catfishing_n_5b44f652e4b048036ea342fc.
- ↑ Tegtmeyer, Lauren. “The Lies We Tell On Dating Apps.” Bustle, Bustle, 30 Oct. 2020, https://www.bustle.com/life/the-lies-we-tell-on-dating-apps.
- ↑ Timmermans, Elisabeth, Elien De Caluwé, and Cassandra Alexopoulos. "Why Are You Cheating on Tinder? Exploring Users' Motives and (dark) Personality Traits." Computers in Human Behavior, Dec. 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.07.040.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Kelly, Heather. “Dating app Hinge cracks down on cheaters.” CNN Business, Cable News Network, 15 May 2015, https://money.cnn.com/2015/05/14/technology/hinge-relationship-status/index.html.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 Hinge. “Privacy.” Hinge, hinge.co/privacy.html.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 36.4 36.5 Goldberg, N. (19 March 2021). NYC blind woman sues Hinge in federal court, says she can’t use dating app, Retrieved 20 March 2021, from https://www.nydailynews.com/new-york/ny-blind-woman-sues-hinge-app-not-accessible-dating-20210319-p5rh7gxwlbe75ac3th6dpnqoni-story.html
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 37.3 Smothers, Hannah. “This Controversial New Dating App Feature Allows You to Choose Which Ethnicities You See.” Cosmopolitan, Cosmopolitan, 9 Oct. 2017, www.cosmopolitan.com/sex-love/a7204682/hinge-ethnicity-preference/.