Difference between revisions of "Fast Fashion"
(changed headings to be decending) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
===Implementation of AI=== | ===Implementation of AI=== | ||
| − | AI is becoming the fore-front force in fast fashion practices. From design, manufacturing, logistic supply chain, and marketing, AI in the fashion industry is starting to transform how companies operate and maximize their profits. In the age of digitalization, AI and machine learning (ML) based technologies are providing automated solutions to provide the most efficient, cost-saving methods | + | AI is becoming the fore-front force in fast fashion practices. From design, manufacturing, logistic supply chain, and marketing, AI in the fashion industry is starting to transform how companies operate and maximize their profits. In the age of digitalization, AI and machine learning (ML) based technologies are providing automated solutions to provide the most efficient, cost-saving methods. |
| + | ====Designing Clothes==== | ||
| + | AI can act as a clothing designer because it can reduce forecasting errors by detecting new, in-demand trends. Because fashion trends vary on such a fast face, AI designers need to keep up with the latest styles by analyzing designs through images to copying those popular styles. <ref> Bisen, V. (18 January 2020). How AI is Changing Fashion: Impact on the Industry with Use Cases. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://medium.com/vsinghbisen/how-ai-is-changing-fashion-impact-on-the-industry-with-use-cases-76f20fc5d93f </ref>. | ||
| + | ====Manufacturing==== | ||
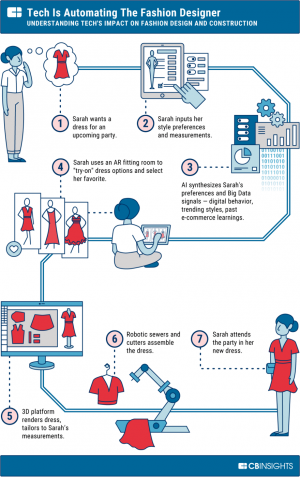
AI also plays a role in manufacturing and supply chains. AI can perform labor-intensive tasks such as sewing and sorting with a faster speed and accuracy, therefore reducing the extra cost of employees. Fast fashion companies can also mass-produce their clothing because AI-enabled machines and robots can perfectly stitch the fabrics while detecting any faults in the material. In inventory and supply chain management, AI speeds up the routes the products take by cutting the logistic supplies and shipping costs. Using these benefits provided by AI, companies can have specific logistics and supply chain processes that offer faster delivery options and can find alternate routes for vehicles if derailed by unforeseen circumstances. <ref> Schmelzer, R. (16 July 2019). The Fashion Industry is Getting More Intelligent with AI. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/07/16/the-fashion-industry-is-getting-more-intelligent-with-ai/?sh=15d0d973c74d </ref>. Manufacturing marketplaces can also utilize AI to assess whether or not designs are feasible and can provide estimates on cost and production time, which potentially eliminates long periods of communication with suppliers. This is a crucial role for mass production because the more products they can create and send out ultimately equals more profit for the business. Now, vendors tend to be less responsive to small-quantity orders unless they are specifically set up for that scale because of the shift towards mass production and the use of AI methods. <ref> CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion </ref>. | AI also plays a role in manufacturing and supply chains. AI can perform labor-intensive tasks such as sewing and sorting with a faster speed and accuracy, therefore reducing the extra cost of employees. Fast fashion companies can also mass-produce their clothing because AI-enabled machines and robots can perfectly stitch the fabrics while detecting any faults in the material. In inventory and supply chain management, AI speeds up the routes the products take by cutting the logistic supplies and shipping costs. Using these benefits provided by AI, companies can have specific logistics and supply chain processes that offer faster delivery options and can find alternate routes for vehicles if derailed by unforeseen circumstances. <ref> Schmelzer, R. (16 July 2019). The Fashion Industry is Getting More Intelligent with AI. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/07/16/the-fashion-industry-is-getting-more-intelligent-with-ai/?sh=15d0d973c74d </ref>. Manufacturing marketplaces can also utilize AI to assess whether or not designs are feasible and can provide estimates on cost and production time, which potentially eliminates long periods of communication with suppliers. This is a crucial role for mass production because the more products they can create and send out ultimately equals more profit for the business. Now, vendors tend to be less responsive to small-quantity orders unless they are specifically set up for that scale because of the shift towards mass production and the use of AI methods. <ref> CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion </ref>. | ||
[[File:techinfashion.png|thumbnail|left|AI Production in Fast Fashion|<ref> CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion </ref>]] | [[File:techinfashion.png|thumbnail|left|AI Production in Fast Fashion|<ref> CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion </ref>]] | ||
| + | ====Virtual Fitting Rooms==== | ||
| + | AI also provides virtual fitting rooms in which customers can virtually try on items. To achieve this, consumers provide their personal data such as their height, weight, and fit preferences, and this information is used in conjunction with AI and 3D cameras. These algorithms combine customer information with existing databases of various items, styles, and sizes to recommend the best products from brand partners to consumers. This allows for personalized recommendations and easier access to products with contactless methods. <ref> Shemar, K. (August 2020). Fashion & AI: the privacy of virtual fitting rooms. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.gerrishlegal.com/legal-blog/2020/9/8/fashion-amp-ai-the-privacy-of-virtual-fitting-rooms </ref>. | ||
| − | |||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Revision as of 17:02, 17 March 2021
Fast-Fashion is a popular business model that focuses on mass production, design, and marketing. The manufacturing relies on replicating trendy styles and low-quality materials to produce inexpensive clothing styles for the general public. These cheaply-made, trendy pieces have resulted in a large-scale movement within the fashion industry. [1]. The earliest version of fast fashion starts back in the 1960s with the paper clothing trend, where one viral marketing campaign instigated the movement through paper napkins. [2]. Scott Paper Company initially tried to sell napkins and toilet paper to promote its new Dura-Weve material. Instead, two styles of shift dress emerged from this type of paper. In eight months, 500,000 units were sold, which prompted fast-fashion business models during the late 20th century to manufacture cloth cheaper and more efficiently, utilizing new materials like polyester and nylon. This movement spawned other new methods that fast fashion is known for: efficient supply chains, highly responsive manufacturing methods, inexpensive labor in sweatshop production, and low-labor bulk manufacturing industries in South, South East, and East Asia. [3]. Companies like Uniqlo, H&M, and Zara built these business models, based on inexpensive clothing from efficient production lines, to create more seasonal/trendy designs that are continuously marketed to fashion-conscious consumers. [4].
Contents
Technology in Fast Fashion Practices
Data Collection
Nowadays, fashion brands, including fast fashion and high-brand names use modern technology to understand their market and customers better. Through online data collection, some companies can use artificial intelligence to reshape the company's approach to product design and development, which allows them to predict what customers will want to look for and buy next. [6]. Big data analysis has already begun to take on a significant role in forecasting customer behavior and buying patterns. The brands with the resources and funds to obtain these analytics have a competitive edge over other smaller businesses. Because of these big data analytics, fast fashion brands can revamp their marketing tactics to find and create the best, most profitable products to bring to their consumers. Currently, to be successful within the fashion industry, brands need to predict fashion and industry trends to stay in touch with the ever-changing consumer preferences. [7]. Big Data analytics can provide companies many useful services, mainly through analyzing trends, identifying target markets, and improving cross-selling. Helping companies understand market trends by using data-driven sentiment analysis solutions on social media and other platforms ultimately aids them in marketing their products correctly.
Implementation of AI
AI is becoming the fore-front force in fast fashion practices. From design, manufacturing, logistic supply chain, and marketing, AI in the fashion industry is starting to transform how companies operate and maximize their profits. In the age of digitalization, AI and machine learning (ML) based technologies are providing automated solutions to provide the most efficient, cost-saving methods.
Designing Clothes
AI can act as a clothing designer because it can reduce forecasting errors by detecting new, in-demand trends. Because fashion trends vary on such a fast face, AI designers need to keep up with the latest styles by analyzing designs through images to copying those popular styles. [8].
Manufacturing
AI also plays a role in manufacturing and supply chains. AI can perform labor-intensive tasks such as sewing and sorting with a faster speed and accuracy, therefore reducing the extra cost of employees. Fast fashion companies can also mass-produce their clothing because AI-enabled machines and robots can perfectly stitch the fabrics while detecting any faults in the material. In inventory and supply chain management, AI speeds up the routes the products take by cutting the logistic supplies and shipping costs. Using these benefits provided by AI, companies can have specific logistics and supply chain processes that offer faster delivery options and can find alternate routes for vehicles if derailed by unforeseen circumstances. [9]. Manufacturing marketplaces can also utilize AI to assess whether or not designs are feasible and can provide estimates on cost and production time, which potentially eliminates long periods of communication with suppliers. This is a crucial role for mass production because the more products they can create and send out ultimately equals more profit for the business. Now, vendors tend to be less responsive to small-quantity orders unless they are specifically set up for that scale because of the shift towards mass production and the use of AI methods. [10].
Virtual Fitting Rooms
AI also provides virtual fitting rooms in which customers can virtually try on items. To achieve this, consumers provide their personal data such as their height, weight, and fit preferences, and this information is used in conjunction with AI and 3D cameras. These algorithms combine customer information with existing databases of various items, styles, and sizes to recommend the best products from brand partners to consumers. This allows for personalized recommendations and easier access to products with contactless methods. [12].
References
- ↑ Linden, A. (2016). An Analysis of the Fast Fashion Industry. Retrieved 10 March 2021, from https://digitalcommons.bard.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1033&context=senproj_f2016
- ↑ Buck, S. (27 November 2017). This wild paper clothing trend of the 1960s was the early version of fast fashion. Retrieved 11 March 2021, from https://timeline.com/paper-fashion-1960s-43dd00590bce
- ↑ Joy, A. (2012). Fast Fashion, Sustainability, and the Ethical Appeal of Luxury Brands. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www3.nd.edu/~jsherry/pdf/2012/FastFashionSustainability.pdf
- ↑ Gustashaw, M. (20 March 2017). Uniqlo Is Going to Start Producing Clothing at Zara Speeds. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.gq.com/story/uniqlo-fast-fashion-speed-zara-competition
- ↑ Stanton, A. (2019). What is Fast Fashion Anyway? Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.thegoodtrade.com/features/what-is-fast-fashion
- ↑ CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion
- ↑ Business Wire. (12 June 2020). How Big Data Analytics Is Changing the Face of Fashion Retail. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200612005108/en/How-Big-Data-Analytics-Is-Changing-the-Face-of-Fashion-Retail-Quantzig%E2%80%99s-Experts-Share-Valuable-Insights-in-Their-Recent-Article#:~:text=In%20the%20fashion%20industry%2C%20data,customer%20behavior%20and%20buying%20patterns.&text=Big%20data%20analytics%20is%20helping,to%20bring%20to%20the%20market
- ↑ Bisen, V. (18 January 2020). How AI is Changing Fashion: Impact on the Industry with Use Cases. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://medium.com/vsinghbisen/how-ai-is-changing-fashion-impact-on-the-industry-with-use-cases-76f20fc5d93f
- ↑ Schmelzer, R. (16 July 2019). The Fashion Industry is Getting More Intelligent with AI. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/07/16/the-fashion-industry-is-getting-more-intelligent-with-ai/?sh=15d0d973c74d
- ↑ CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion
- ↑ CB Insights. (13 October 2020). The Future Of Fashion: From Design To Merchandising, How Tech Is Reshaping The Industry. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.cbinsights.com/research/fashion-tech-future-trends/#:~:text=And%20today%2C%20fashion%20technology%20is,up%20every%20aspect%20of%20fashion
- ↑ Shemar, K. (August 2020). Fashion & AI: the privacy of virtual fitting rooms. Retrieved 12 March 2021, from https://www.gerrishlegal.com/legal-blog/2020/9/8/fashion-amp-ai-the-privacy-of-virtual-fitting-rooms