Cloud Computing
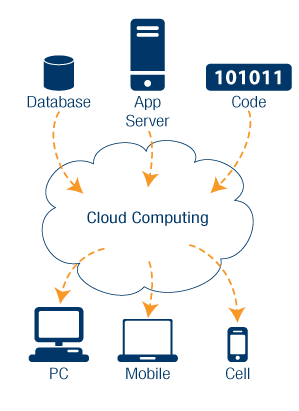
Cloud computing is the practice of offering shared computational resources to end-users by way of remote servers. Its basic premise includes offering storage, management, and processing of data to an end-user from a centralized location, without the need of powerful individual terminals to carry out computational tasks.[1] Transfer of the processed data files, in the form of documents, emails, or applications can then occurs over a network connection.
Access and delivery of data is done through applications such as web browsers[2], which require far lower computational resources than individual terminals. The dispersal of computational resources from a central location is intended to be more cost-effective than individualized-terminal forms of computing.[3]
Contents
Overview
Cloud computing delivers computational capability from a centralized source to an end-user via an internet connection. Once the connection from host to end-user is made through the connection, multiple differing levels of service can be achieved based on the user’s needs and the system’s specifications.
Layers of Cloud Computing
Shared cloud computing resources range from simple applications, in which users only have access to the functions provided by the application, all the way to shared operating systems which are run remotely on the server. The levels of software abstraction available to the user through the cloud are relative to the purpose of system.
“Software as a Service”
Through the process of centralized computation, cloud computing embodies a new model for the delivery of computational resources. Cloud computing often employs “Software as a Service” (SaaS), in which software is “delivered” to end-users by way of network connections as opposed to being carried out locally. Contrasted with software being seen as a static part of the computational process, this shift in paradigm allows software’s computational nature to be seen as a resource.
Benefits
Characteristics
When companies hire new employees they must install various software packages onto their computers. This usually is a long and tiresome process because many of these packages require certain product licensing numbers. However with cloud computing they can establish an internal network where they can simply access these required programs with ease because they are stored online in the cloud network. This is quicker and easier than manually downloading them onto each specific computer.
Flexible
This users and/or companies can determine how much space they want to store on their network. The amount of space consumed ranges on the user’s needs.
User Friendly
Users can oversee services and have them automatically updated to accommodate their storage, processing, and software needs.
Reasonable
Users are only billed for the resources they use such as space consumed and processing capability.
Convenience
Apple recently announced that as of October 12, 2011 that their iCloud will be available to users thus making it easier to manage data across a variety of their products such as the iPod, iPhone, and iPad. iCloud allows users to store their content, music, photos, documents, and files in one virtual location that can be accessed by the various apple devices mentioned previously. In addition to Apple's iCloud, Dropbox also offers a similar storage service for your music, photos, and important documents. These services have revolutionized and upgraded the utility and attractiveness of cloud computing for the average consumer. By offering a safe place to back-up files and storage, it allows consumers and companies to increase storage and capability without investing capital into new servers, infrastructure, information technology services, and licensing. Cloud computing eliminates the costly overhead for subscription servers and pay-per-use services, extending information technology's reach across the internet. Cloud services provide these ample, but innovative conveniences for users.
Ethical Implications
There are many ethical concerns with the development of new and revolution technologies such as cloud computing. One of the largest concerns deals with the illegal exchange and sharing of information (see Digital Piracy) between users on the same cloud interface. This issue is hotly debated and difficult to resolve due to various copyright and licensing regulations. Cloud computing presents users with ethical dilemmas about whether or not to illegal gain access to certain materials whether it be media files, movies, or software.