Difference between revisions of "Stop Online Piracy Act"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
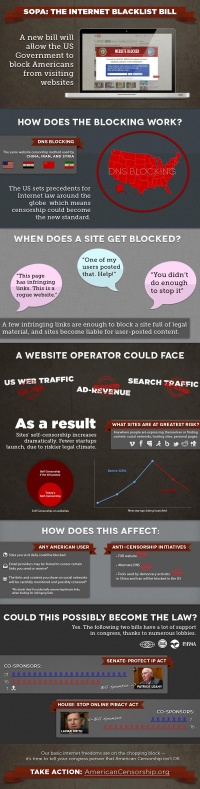
| − | [[File:sopa infographic.jpg|200px|thumb|right|An opinionated SOPA infographic]]The Stop Online Piracy Act, or SOPA is a proposed bill in the United States House of Representatives. The US Senate's version of SOPA is called The Protect IP Act,or PIPA. The bill would target websites that distribute infringing materials by having the Department of Justice (DoJ) block those websites with DNS, or Domain Name Service blocking <ref name="pub"> http://www.publicknowledge.org/blog/sopa-immunity-net-neutrality-violations </ref>. | + | [[File:sopa infographic.jpg|200px|thumb|right|An opinionated SOPA infographic]]The Stop Online Piracy Act, or SOPA is a proposed bill in the United States House of Representatives. The US Senate's version of SOPA is called The Protect IP Act,or PIPA. The bill would target websites that distribute infringing materials by having the Department of Justice (DoJ) block those websites with DNS, or Domain Name Service blocking <ref name="pub"> http://www.publicknowledge.org/blog/sopa-immunity-net-neutrality-violations </ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Overview of the Act== | ||
| + | The Stop Online Piracy Act works by blocking websites that enable or facilitate copyright infringement. With SOPA, rights-holders can demand that payment vendors and ad networks end relationships with infringing websites <ref name = "huff"> http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2011/11/18/stop-online-privacy-act-small-business_n_1102322.html </ref>. The U.S. Government may also seek a court order requiring ISPs and search engines to block consumer access </ref name = "huff">. | ||
==DNS Blocking== | ==DNS Blocking== | ||
Revision as of 01:48, 29 November 2011
The Stop Online Piracy Act, or SOPA is a proposed bill in the United States House of Representatives. The US Senate's version of SOPA is called The Protect IP Act,or PIPA. The bill would target websites that distribute infringing materials by having the Department of Justice (DoJ) block those websites with DNS, or Domain Name Service blocking [1].Overview of the Act
The Stop Online Piracy Act works by blocking websites that enable or facilitate copyright infringement. With SOPA, rights-holders can demand that payment vendors and ad networks end relationships with infringing websites [2]. The U.S. Government may also seek a court order requiring ISPs and search engines to block consumer access </ref name = "huff">.
DNS Blocking
The SOPA bill would work by blocking DNS requests. A DNS request works by translating a URL into a numeric ip address, and the bill allow the government to redirect the URL to a different page, likely a page displaying a message from the government </ref name = "pub">. While the aim of DNS blocking is to block access to sites, there are ways to easily bypass DNS blocking. If the numeric ip address can be obtained, access to the site is still available, though it would be illegal. There also exist plug-ins for bypassing DNS blocking, such as the MAFIAAFire add-on for the Mozilla Firefox browser. Using a proxy server or a VPN are also ways to bypass the DNS block [3].