Difference between revisions of "Dark Web"
(added intro) |
(modified ethical concerns with dark web section) |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The Dark Web is a sector of the World Wide Web that requires specific software to access and | + | [[File:Dark web.jpg|400px|right]] |
| + | |||
| + | The '''Dark Web''' is a sector of the World Wide Web that requires specific software to access. Hailed as one of the last remaining safe-havens for complete anonymity, the Dark Web continues to garner attention and press worldwide. In order to access the Dark Web, certain protocols must be followed--most notably including the use of Tor. Tor is a software package and network structure that is used to run the Dark Web. Users can visit websites that are not crawled or indexed by search engines, such as Google, and they can keep their activity hidden and anonymous by using multiple levels of servers to route information through advanced encryption technology. Due to the ability of the Dark Web to completely hide someone's identity, however, the use of the service often strays into illegality. The Dark Web is criticized for facilitating illegal activity by providing a place for criminals to carry out their methods and deals. Ethical issues have also risen since the rise of the Dark Web: including but not limited to hosting illegal platforms, like the Silk Road, and providing a place for terrorist organizations and individual pedophiles to plan out and execute illegal acts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==History== | ||
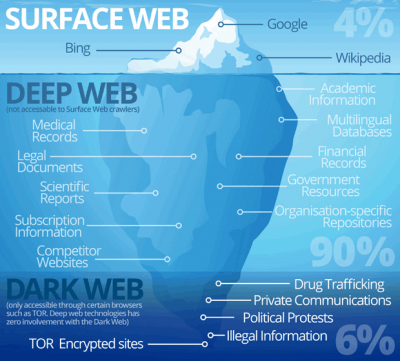
| + | [[File:Darkweb.png|400px|right|thumbnail| the location of the dark web in context to the rest of the internet]] | ||
| + | The Dark Web has origins that can be traced all the way back to 1969,<ref>The Darknet: A Short History, Ty McCormick, 9 December 2013 [http://foreignpolicy.com/2013/12/09/the-darknet-a-short-history/ foreignpolicy.com]</ref> when a Pentagon-funded program was able to transmit simple messages over secretive networks known collectively as ARPANET. Following these early attempts to transmit and store secretive data, there were also plans in the 1980’s and 90s to collect illegal data and keep them in safe havens, most notably in the Caribbean.<ref>The Darknet: A Short History, Ty McCormick, 9 December 2013 [http://foreignpolicy.com/2013/12/09/the-darknet-a-short-history/ foreignpolicy.com]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, it was not until 2002 that a more suitable format was developed for accessing the deeper reaches of the World Wide Web. Worked on since the mid-90s, an open-source software was released to the public under the name “Tor.” Developed by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory<ref>The Unlikely History of Tor, Paul Hill, 14 February 2018 [https://www.expressvpn.com/internet-privacy/tor/history/ expressvpn.com]</ref>, it is still unclear why the U.S. government decided to release the project to the public. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==How Tor Works== | ||
| + | Based on the concept of Onion Routing<ref> https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Onion_routing</ref>, Tor makes a user anonymous on the Internet by encrypting data going in and out of one’s IP address and subsequently routing this encrypted information through multiple servers.<ref>Everything About Tor: What is Tor? How Tor Works?, Aditya Tiwari, 22 May 2017 [https://fossbytes.com/everything-tor-tor-tor-works/ expressvpn.com]</ref> Once the data reaches the last layer of Tor servers, any sort of tracking or surveillance software traces the source of the content to this exit point, not the individual user. Thus, much like an onion, these multiple layers allow an identity to be hidden on the Internet as it cannot be easily traced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Whistleblowers and the Dark Web== | ||
| + | However, it also allows more popular sites to survive and remain on the web even when faced by national security threats. For instance, the popular whistleblowing site [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WikiLeaks Wikileaks], which aims to release classified government documents to the public, has survived due to the Dark Web.<ref>What's Hiding In The Dark Web?, Ed Smith, 4 April 2017 [https://www.truthfinder.com/infomania/technology/deep-web-search/]</ref> Facebook is another example of a technological giant who makes use of the Tor database to allow its user to remain anonymous and avoid surveillance.<ref>What's Hiding In The Dark Web?, Ed Smith, 4 April 2017 [https://www.truthfinder.com/infomania/technology/deep-web-search/]</ref> | ||
| + | It can be argued that Tor and the Dark Web itself is a powerful tool that can help combat government surveillance and keep the possibility of total government control nearly impossible. Responsible usage of services like Tor can create a safe online space for users where they do not have to worry about their data being mined, sold, or bought by large-scale corporations. However, support has been difficult to garner for the Dark Web even with the potential upsides that this domain provides, the lack of security and safety navigating through it makes it difficult to achieve widespread support. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ethical Concerns With the Dark Web== | ||
| + | With over 57% of sites on Tor dedicated for criminal and illegal activity, | ||
| + | <ref>How the dark web is used to sell illegal drugs like fentanyl, Katie Dangerfield, 24 May 2017 [https://globalnews.ca/news/3461998/how-the-dark-web-is-used-to-sell-illegal-drugs-like-fentanyl/]</ref> the presence of the Dark Web has raised significant controversy among internet users. It promotes anonymity and privacy, but also allows high-level criminals and organizations to engage in criminal activity. However, there does not seem to be a solution in sight for stopping this activity. As long as Tor remains in place, there is not much that government agencies can do to slow this surge of crime. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The issue of privacy vs. legality is the most extensive argument built upon the formation of the Dark Web. If any sort of agency were to somehow gain access to Tor services, the entire operation would not be able to protect itself from surveillance and would ultimately become useless. For now, law enforcement can only hope for slip-ups and blunders, which have allowed them to catch criminals in the past, such as arresting Silk Road founder [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ross_Ulbricht Ross William Ulbricht] in 2013. <ref>Hume, T. (2013, October 05). How the FBI caught Ross Ulbricht, alleged creator of Silk Road. Retrieved from https://www.cnn.com/2013/10/04/world/americas/silk-road-ross-ulbricht/index.html</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Illegal Activities=== | ||
| + | Due to the level of anonymity, the Dark Web is notorious for hosting illegal activity and trading. The Dark Web aids in connecting users who desire to buy and sell illegal things. It digitized the black market, creating a virtual platform where things can be purchased. Drug trafficking is one of the largest markets on the Dark Web. Before it was shut down in 2013,[7] the Silk Road had nearly $1.2 billion in total sales.[8] Users are able to buy, sell, and ship products around the world without being traced. One large-scale effect the Dark Web has created is the impact on the Afghanistani opium trade, which now relies on the anonymity provided to ship their product around the world.[9] Private vendors globally can take advantage of the Dark Web to ship their product to nearly anyone. Often packaged in ordinary manila envelopes or small packages, drugs are concealed in such a way that they do not tip off the authorities while being shipped. In Canada, for instance, packages shipped domestically cannot be searched without a warrant or reasonable suspicion,<ref>Inside the dark web drug trade, Reid Southwick, 21 May 2016 [https://newsinteractives.cbc.ca/longform/the-new-frontier-of-the-drug-trade]</ref> which has opened up an entirely new section of users that can obtain drugs from the comfort of their own home. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Arms trafficking is another large-scale operation that has exploded in the popularity through the Dark Web. With 59.9% of all Dark Web arms trafficking coming from the U.S, [10] it is a major issue for gun enforcement agencies around the world. Users are able to buy weapons ranging from pistols to explosives. Almost every type of weapon is able to be found on the Dark Web. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Dark Web also has other illegal activities such as hitmen for hire, human trafficking, and smuggling goods that are illegal in certain countries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Furthermore, the Dark Web hosts services such as counterfeit passports and IDs, social networks only created to share and distribute child pornography, and even hitmen available for hire.[11] Almost any known illegal activity can be found on the Dark Web for a price. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Terrorist Activities=== | ||
| + | On top of other socially damaging illegal activities, the Dark Web is also host to several colluding terrorist organizations. The organization of these groups is made easier by the extreme anonymity of the Deep Web and the inability of government agencies to efficiently track their activities. The Dark Web serves not only as a means for terrorists organizations to communicate their plans of attack, they also provide a means for the spread of methodologies and the recruitment of new members.<ref>Terrorists use the Dark Web to hide, [https://www.usatoday.com/story/tech/news/2017/03/27/terrorists-use-dark-web-hide-london-whatsapp-encryption/99698672/]</ref> It is because of the difficulty that comes with monitoring such activity that there are programs and research projects in progress that are dedicated to finding more efficient methods of gathering information on potential terrorist groups.<ref> Uncovering the dark Web: A case study of Jihad on the Web., [https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Uncovering-the-dark-Web%3A-A-case-study-of-Jihad-on-Chen-Chung/1cdbf367e1b456e9b758aa0fdcf004fb53074a6d?tab=citations]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Scams & Hoaxes=== | ||
| + | Due to the total anonymity and the nature of the Dark Web, any activity is essentially totally unregulated and there is minimal, if any, accountability present. Thus, the Dark Web has become the ideal host for hoaxes, fraud services, scams, and unverified content. Numerous carding forums and counterfeiting services exist in the sector, yet a substantial percentage of such sites are scams in themselves. Many sites and darknet markets link to fraudulent URLs. Additionally, even many assassination and hitman services have been found to be scams. An urban legend tells of the "Red Room", where one would be able to find live murder on the Dark Web. However, deeper examination of direct evidence appears to indicate any reported cases of the "Red Room" were untrue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bitcoin Laundering=== | ||
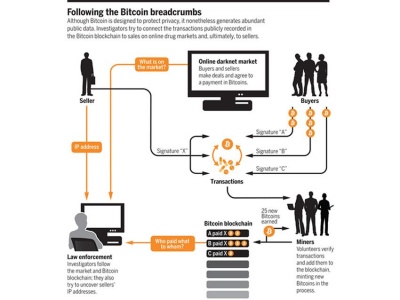
| + | [[File:Bitcoinops.jpg|400px|left|thumbnail| the circular flow of bitcoin activity]] | ||
| + | As a virtual source of currency, Bitcoin runs the majority of deals and transactions on the Dark Web. For reference, illegal drug sales often reach close to or over $100 million a year, and Bitcoin is almost exclusively used for all of these sales.<ref>What Is The Dark Web?, N/A, 4 July 2017 [https://theconversation.com/explainer-what-is-the-dark-web-46070]</ref> | ||
| + | Services such as [https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Bitcoin_Laundry Bitcoin Laundries], allow users on the Dark Web to send Bitcoin transactions to a 3rd party who then in turn send the same amount to the buyer, thus making it almost completely impossible to track the original buyer. Before Bitcoin, it was extremely difficult to facilitate any sort of trade on the Dark Web safely. The arrival of Bitcoin has paved the way for new markets and transactions to emerge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==In popular culture== | ||
| + | ''Stitchers'', a science-fiction crime drama show on Freeform (formerly ABC Family), had an episode in the third season where the case involved a hit-man for hire website on the Dark Web. In the show, the website, "ALL IN" let the characters pick one person they would like to be killed. In return, they were required to kill somebody else. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In CBS crime-drama, ''Criminal Minds'', FBI technical analyst and former hacker, Penelope Garcia has to sometimes go back into the underground hacker network and her contacts in the Dark Web. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Agents of Shield'' character, Skye (now Daisy Johnson), is a prominent member of the Rising Tide, an anonymous hacker organization that is keen on revealing the government's classified secrets such as the secrets of Iron Man, Hulk, and Thor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:27, 19 April 2019
The Dark Web is a sector of the World Wide Web that requires specific software to access. Hailed as one of the last remaining safe-havens for complete anonymity, the Dark Web continues to garner attention and press worldwide. In order to access the Dark Web, certain protocols must be followed--most notably including the use of Tor. Tor is a software package and network structure that is used to run the Dark Web. Users can visit websites that are not crawled or indexed by search engines, such as Google, and they can keep their activity hidden and anonymous by using multiple levels of servers to route information through advanced encryption technology. Due to the ability of the Dark Web to completely hide someone's identity, however, the use of the service often strays into illegality. The Dark Web is criticized for facilitating illegal activity by providing a place for criminals to carry out their methods and deals. Ethical issues have also risen since the rise of the Dark Web: including but not limited to hosting illegal platforms, like the Silk Road, and providing a place for terrorist organizations and individual pedophiles to plan out and execute illegal acts.
Contents
History
The Dark Web has origins that can be traced all the way back to 1969,[1] when a Pentagon-funded program was able to transmit simple messages over secretive networks known collectively as ARPANET. Following these early attempts to transmit and store secretive data, there were also plans in the 1980’s and 90s to collect illegal data and keep them in safe havens, most notably in the Caribbean.[2]
However, it was not until 2002 that a more suitable format was developed for accessing the deeper reaches of the World Wide Web. Worked on since the mid-90s, an open-source software was released to the public under the name “Tor.” Developed by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory[3], it is still unclear why the U.S. government decided to release the project to the public.
How Tor Works
Based on the concept of Onion Routing[4], Tor makes a user anonymous on the Internet by encrypting data going in and out of one’s IP address and subsequently routing this encrypted information through multiple servers.[5] Once the data reaches the last layer of Tor servers, any sort of tracking or surveillance software traces the source of the content to this exit point, not the individual user. Thus, much like an onion, these multiple layers allow an identity to be hidden on the Internet as it cannot be easily traced.
Whistleblowers and the Dark Web
However, it also allows more popular sites to survive and remain on the web even when faced by national security threats. For instance, the popular whistleblowing site Wikileaks, which aims to release classified government documents to the public, has survived due to the Dark Web.[6] Facebook is another example of a technological giant who makes use of the Tor database to allow its user to remain anonymous and avoid surveillance.[7] It can be argued that Tor and the Dark Web itself is a powerful tool that can help combat government surveillance and keep the possibility of total government control nearly impossible. Responsible usage of services like Tor can create a safe online space for users where they do not have to worry about their data being mined, sold, or bought by large-scale corporations. However, support has been difficult to garner for the Dark Web even with the potential upsides that this domain provides, the lack of security and safety navigating through it makes it difficult to achieve widespread support.
Ethical Concerns With the Dark Web
With over 57% of sites on Tor dedicated for criminal and illegal activity, [8] the presence of the Dark Web has raised significant controversy among internet users. It promotes anonymity and privacy, but also allows high-level criminals and organizations to engage in criminal activity. However, there does not seem to be a solution in sight for stopping this activity. As long as Tor remains in place, there is not much that government agencies can do to slow this surge of crime.
The issue of privacy vs. legality is the most extensive argument built upon the formation of the Dark Web. If any sort of agency were to somehow gain access to Tor services, the entire operation would not be able to protect itself from surveillance and would ultimately become useless. For now, law enforcement can only hope for slip-ups and blunders, which have allowed them to catch criminals in the past, such as arresting Silk Road founder Ross William Ulbricht in 2013. [9]
Illegal Activities
Due to the level of anonymity, the Dark Web is notorious for hosting illegal activity and trading. The Dark Web aids in connecting users who desire to buy and sell illegal things. It digitized the black market, creating a virtual platform where things can be purchased. Drug trafficking is one of the largest markets on the Dark Web. Before it was shut down in 2013,[7] the Silk Road had nearly $1.2 billion in total sales.[8] Users are able to buy, sell, and ship products around the world without being traced. One large-scale effect the Dark Web has created is the impact on the Afghanistani opium trade, which now relies on the anonymity provided to ship their product around the world.[9] Private vendors globally can take advantage of the Dark Web to ship their product to nearly anyone. Often packaged in ordinary manila envelopes or small packages, drugs are concealed in such a way that they do not tip off the authorities while being shipped. In Canada, for instance, packages shipped domestically cannot be searched without a warrant or reasonable suspicion,[10] which has opened up an entirely new section of users that can obtain drugs from the comfort of their own home.
Arms trafficking is another large-scale operation that has exploded in the popularity through the Dark Web. With 59.9% of all Dark Web arms trafficking coming from the U.S, [10] it is a major issue for gun enforcement agencies around the world. Users are able to buy weapons ranging from pistols to explosives. Almost every type of weapon is able to be found on the Dark Web.
The Dark Web also has other illegal activities such as hitmen for hire, human trafficking, and smuggling goods that are illegal in certain countries.
Furthermore, the Dark Web hosts services such as counterfeit passports and IDs, social networks only created to share and distribute child pornography, and even hitmen available for hire.[11] Almost any known illegal activity can be found on the Dark Web for a price.
Terrorist Activities
On top of other socially damaging illegal activities, the Dark Web is also host to several colluding terrorist organizations. The organization of these groups is made easier by the extreme anonymity of the Deep Web and the inability of government agencies to efficiently track their activities. The Dark Web serves not only as a means for terrorists organizations to communicate their plans of attack, they also provide a means for the spread of methodologies and the recruitment of new members.[11] It is because of the difficulty that comes with monitoring such activity that there are programs and research projects in progress that are dedicated to finding more efficient methods of gathering information on potential terrorist groups.[12]
Scams & Hoaxes
Due to the total anonymity and the nature of the Dark Web, any activity is essentially totally unregulated and there is minimal, if any, accountability present. Thus, the Dark Web has become the ideal host for hoaxes, fraud services, scams, and unverified content. Numerous carding forums and counterfeiting services exist in the sector, yet a substantial percentage of such sites are scams in themselves. Many sites and darknet markets link to fraudulent URLs. Additionally, even many assassination and hitman services have been found to be scams. An urban legend tells of the "Red Room", where one would be able to find live murder on the Dark Web. However, deeper examination of direct evidence appears to indicate any reported cases of the "Red Room" were untrue.
Bitcoin Laundering
As a virtual source of currency, Bitcoin runs the majority of deals and transactions on the Dark Web. For reference, illegal drug sales often reach close to or over $100 million a year, and Bitcoin is almost exclusively used for all of these sales.[13] Services such as Bitcoin Laundries, allow users on the Dark Web to send Bitcoin transactions to a 3rd party who then in turn send the same amount to the buyer, thus making it almost completely impossible to track the original buyer. Before Bitcoin, it was extremely difficult to facilitate any sort of trade on the Dark Web safely. The arrival of Bitcoin has paved the way for new markets and transactions to emerge.
In popular culture
Stitchers, a science-fiction crime drama show on Freeform (formerly ABC Family), had an episode in the third season where the case involved a hit-man for hire website on the Dark Web. In the show, the website, "ALL IN" let the characters pick one person they would like to be killed. In return, they were required to kill somebody else.
In CBS crime-drama, Criminal Minds, FBI technical analyst and former hacker, Penelope Garcia has to sometimes go back into the underground hacker network and her contacts in the Dark Web.
Agents of Shield character, Skye (now Daisy Johnson), is a prominent member of the Rising Tide, an anonymous hacker organization that is keen on revealing the government's classified secrets such as the secrets of Iron Man, Hulk, and Thor.
References
- ↑ The Darknet: A Short History, Ty McCormick, 9 December 2013 foreignpolicy.com
- ↑ The Darknet: A Short History, Ty McCormick, 9 December 2013 foreignpolicy.com
- ↑ The Unlikely History of Tor, Paul Hill, 14 February 2018 expressvpn.com
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Onion_routing
- ↑ Everything About Tor: What is Tor? How Tor Works?, Aditya Tiwari, 22 May 2017 expressvpn.com
- ↑ What's Hiding In The Dark Web?, Ed Smith, 4 April 2017 [1]
- ↑ What's Hiding In The Dark Web?, Ed Smith, 4 April 2017 [2]
- ↑ How the dark web is used to sell illegal drugs like fentanyl, Katie Dangerfield, 24 May 2017 [3]
- ↑ Hume, T. (2013, October 05). How the FBI caught Ross Ulbricht, alleged creator of Silk Road. Retrieved from https://www.cnn.com/2013/10/04/world/americas/silk-road-ross-ulbricht/index.html
- ↑ Inside the dark web drug trade, Reid Southwick, 21 May 2016 [4]
- ↑ Terrorists use the Dark Web to hide, [5]
- ↑ Uncovering the dark Web: A case study of Jihad on the Web., [6]
- ↑ What Is The Dark Web?, N/A, 4 July 2017 [7]