Apple Watch

Apple Watch is a line of smartwatches, or computers that users can wear around their wrists, from the technology company Apple[1] and allows users to perform a variety of tasks [2]. In order to function, the watch needs to be paired with other Apple products, specifically an iPhone5 model or later. [3]. The Apple Watch is equipped with software and hardware capabilities that gives it the ability to interact with the user in a variety of ways.
There are different Apple Watch models that users can choose from, which each offering a unique array of features to the users. In terms of the public perception of the Apple Watch, it has gained both negative and positive feedback from the public, but has overall been a popular product for Apple. In 2020 alone, Apple sold 33.9 million Apple Watches to users, making it a leader in the smartwatch industry over comparable brands like Huawei, Samsung, BBK, and fitbit. [4].
In looking at the ethical considerations of the product, the Apple Watch collects sensitive user data, including health related data. As a device that connects with other Apple products, there are security concerns related to the data that it collects in relation to being a internet of Things device. Further, there are rising concerns that the Apple Watch may intendedly lead to the perpetuation of inequalities in society [5].
Contents
Brief History
The Apple Watch was first released in 2015, with three distinct models; however, the genesis of the Apple Watch reportedly started with Jony Ive, Apple's chief designer, in 2011. [6]. Ive reportedly began "dreaming about an Apple watch just after CEO Steve Jobs' death in October 2011" and brought to idea to Alan Dye, the chief of Apple's human interface group to put the idea to life [7]. The intention of the watch was to reportedly free people from their phones [8]. The designers of the Apple Watch uncovered early in the process that they needed to break away from Apple's status quo of only offering a few product options as the watch industry values personalization and beauty. That realization spurred the development the watch which offered a variety of options in order to appeal to a way consumer base. [9]
Hardware Capabilities

The hardware installed on the Apple Watch includes a digital crown, friends button, touchscreen, taptic engine, battery, s1 chip, loudspeaker, custom-heart rate sensor, induction charger, and a customizable appearance. The "digital crown," is a small button on the side of the watch that users can rotate and press in order to scroll through and engage with content on their watch [11]. The friends button, located next to the crown on the side of the watch, brings up a shortlist of chosen contacts to the user. The touchscreen is a retina display that allows users to interact with the watches face, through tapping on the small touchscreen interface with their finger. The touchscreen is polished with crystal in order to prevent users from scratching the screen. The taptic engine delivers tactile sensations to the user, and essentially taps the user's wrist to deliver tactile feedback when interfacing with the digital crown or force touch. It also helps notify users of alerts and notifications [12]. The battery allows the watch to run throughout the day without running out of battery. The Apple Watch comes equipped with a charger, which is used to recharge the battery after use. Similar to the iPhone, the Apple Watch typically lasts about a full day's use before needing to recharge, depending on usage. The s1 chip contains the entire computer system needed for the Apple Watch to run. The loudspeaker which has a multidirectional microphone that allows it to listen and process multiple conversations around and involving the user [13]. It allows for the watch to output noise, or speak, to the user as well. The custom heart-rate sensor uses infrared lights and photosensors to read the user's heart rate [14]. This provides users with information on their daily steps, heart rate capabilities, and hours of sleep.
Software Capabilities
Apple watchOS is the software that Apple Watches run on, and is based on iOS. watchOS was released along with the launch of the first Apple Watch in 2015 [15]. Since 2015, Apple has launched watchOS 1, watchOS 2, watchOS 3, watchOS 4, watchOS5, watchOS 6, watchOS 7, and watchOS 8. Each watchOS update offered a variety of new features and capabilities to the watch user. For example, the latest Apple Watch software update, watchOS 8, includes new features such as an updated interface of its wellness app, and updated fall detection algorithms [16].
Communication features
Through the evolution of the watchOS versions, Apple Watch is able to offer an increasing variety of features to its users, allowing them to engage with the watch in their everyday lives. The Apple Watch allows users to see who is calling or texting them at any given time, given that the watch is properly connected to wifi, their nearby iPhone, or is equipped with GPS capabilities. If the Apple Watch model is equipped with GPS capabilities, and the watch has been connected to a wireless plan with a phone provider, the Apple Watch does not need to be near ones phone in order to send and receive calls and text messages. If an Apple Watch does not have cellular connectivity, it will use bluetooth technology to connect to the users nearby iPhone (up to 12 feet away) or through wifi. The "walkie-talkie" feature allows users to connect with other Apple Watch users; however, both Apple Watch users need to have a watchOS 5 operating system or later. [17] In order to use the Walkie-Talkie features, users must send and accept friend invitations through the "Walkie-Talkie app," and then use the touch and hold button to speak directly to other users like a traditional "Walkie-Talkie."
Fitness Tracking
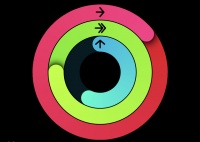
The Apple watch offers fitness tracking in the form of Activity Rings which is broken down into three colored rings. The first is the red Move ring which allows users to track how many calories they have burned by moving throughout a 24 hour period. The second is the green Exercise ring that allows users to track the minutes of brisk activity they have completed that day. Finally, the blue Stand ring allows users to track how many hours they have stood in a 24 hour period. [18] The user can define their activity goals for each type of ring, and the ring visually closes once the user achieves that goal. The visualization shown to the right demonstrates the different types of rings, as well as the users progress in completing the goals associated with each ring.
Apple Watch Models
Since its release in 2015, Apple has released multiple other models which provide different features to the user including Apple Watch Series 1, Apple Watch Series 2, Apple Watch Series 3, Apple Watch Series 4, Apple Watch Series 5, Apple Watch SE, Apple Watch Series 6, and Apple Watch Series 7. The price of an Apple Watch can vary greatly, depending on the model and upgrades that the user would like to purchase. An Apple Watch can be bought through the Apple website starting at $199 for the Series 3 model, and $399 for the Series 7 model [19]. The larger displays (45mm) cost users more compared to the smaller screen displays (41mm). There are also other offered upgrades that will affect the price of the watch.
Apple Watch Series 7
The Apple Watch has evolved over time, offering more high-tech features to its users. The newest Apple Watch, Apple Watch Series 7, offers the most high-technology features to its users through its newest watch software, watchOS8 [20]. In comparing to the first model of the Apple Watch, released in 2015, the Series 1 Apple Watch only had a 8GB capacity, the Series 7 Apple Watch has a 32 GB capacity. Other notable upgrades that the Series 7 Apple Watch offers over the Series 1 Watch includes: 50 percent more screen area, GPS and GPS cellular models, water resistance (up to 50 meters).[21] The Apple Watch Series 7 is marketed as having the largest and most advanced display, being the most durable and fast charging [22]. The newest software offers a few new features to users such as the ability to add vaccination records in user's health app as well as allowing users to better control their home smart devices through the home app [23].
Additional Collaborations
Apple partnered with Nike+ to produce an apple watch for those who are passionate about fitness and the Nike brand. This watch was designed to synchronize with the "Nike Run Club" and "Nike Training Club" apps [24]. Apple partnered with Hermès as well, to create an Apple Watch that emphasized bold, colorful leather bands and exclusive new watch faces for users. [25]
Public Perception
The Apple Watch was first introduced to the public in 2015. The International Data corporation (IDC) highlights that the total sales amount of Apple increased in 2015 [26]. One of the main critiques for the Apple watch upon its debut included its inability to differentiate from similar products, such as the Fitbit.
Fitbit is a brand that offers a lineup of smartwatches that allow users to track personal health data including daily activity, sleep metrics, and other personalized health metrics such as heart rate variability. [27] This smartwatch was released in 2009 [28], and Fitbit's early entry to this untapped market has caused it to be popular to millions of Fitbit devices to be sold worldwide. Yet, while Fitbit was one of the first companies to create a smartwatch with the intent of collecting personalized health data, the Apple Watch has become a more popular smartwatch among users. Specifically, Apple sold 33.9 million watches in 2020, compared to 5.9 million Fitbit watches sold in the same year [29].
Ethical Considerations
The data collection abilities of the Apple Watch have lead to concerns about the privacy and security of user's data. Further, concerns about the potential reliance on health related data as a replacement for professional medical care has been of rising concern. Additionally, there has been rising concern over the lack of security related to Internet of Things devices, such as the Apple Watch. There are concerns that the Apple Watch furthers systems of oppression towards underprivileged populations.
Data Privacy
Big data has emerged in recent years, and is of increasing interest to researchers and organizations anticipating an overwhelming flow of data. The individual privacy surrounding this data is of increasing concern. Data privacy is defined as one's control over access to their own personal information, specifically the right to know what personal information is being dispersed to which people [30]. It is therefore important that users understand the security risks of big data, and understand how companies are protecting and handling user data. Given that the Apple Watch collects multiple types of personal data about the user, the discussion of big data privacy concerns have been relevant to this device.
Privacy legislations are important for prioritizing individual privacy protections, and valuing personal information control, despite business and commercial enterprises' desire to collect data. The access to personal data about users is valuable for companies as they are able to profit from users by customizing their marketing and advertising to the user's preferences. The United States specifically passed the first legislation on information privacy more than 40 years ago through the 1974 US Privacy Act, which developed values related to individual data privacy [31]. This legislation is important for monitoring how companies, like Apple, utilize the big data that is collected from devices like the Apple Watch. Given that the Apple Watch is a device that is intended to connect with other devices, the evolution of the internet of Things has complicated the subject of data privacy. Namely, it is of increasing concern that while data privacy legislation exists, the internet of Things complicates the application of the current legislation. Researchers stress that there are risks of privacy loss and exploitation from internet of Things devices, penalizing owners for accessing the advantages of an increasingly connected world [32]. Given that the Apple Watch is a part of the internet of Things, this is an increasing ethical concern with the device.
Health Related Data
Smartwatches, such as the Apple Watch are equipped with features that allow the user to track health related data. In the medical field, the principle of non maleficence requires that medical actions are weighed against risks, benefits, and consequences [33]. Researchers have argued that the accessibility of a user's own health data has been problematic as it violates the principle of non-maleficence.
For example, ECG monitoring on Apple watches which allows users to screen for atrial fibrillation, with the intent of early detection. Early detection of this arrhythmia can prevent adverse events such as stroke, by treating with anticoagulants. Although the Apple Watch has an algorithm with a very high specificity, many people have still been notified of arrhythmia without having atrial fibrillation, leading to a false positive result [34]. If the patient is not aware of the potential benefits, the risks and the possible consequences of atrial fibrillation detection, the diagnostic can be done at the user's risk. The Apple Watch does not provide any information comparable to traditional medical education, leading the patient to not be medically well-informed, according to researchers. Further, researchers argue that patients could overestimate the accuracy of the diagnostic capabilities of the watch and the over reliance on home monitoring of atrial fibrillation could lead to fewer face-to-face doctor visits. Researchers conclude that the over-reliance on smartwatches and the lower number of face-to-face doctor visits lead to a violation of the principle of non-maleficence. [35].
The American Journal of Medicine highlights the limitations of the health benefits that the Apple Watch can provide through its personalized health data. While wearable devices are designed to promote healthy behaviors and decrease risk for chronic diseases, current literature indicates that wearable devices provide little benefit on chronic disease health outcomes. While the Apple Watch uses marketing techniques to boost a product that will lead to a healthier lifestyle, research has found that while wearable devices can motivate and accelerate physical activity, data does not suggest consistent health benefits [36]. Ethically, scholars fear that the advertising of the product can be misleading to customers with chronic diseases, as they overestimate the value that the product can provide by offering personalized health data.
Internet of Things
The internet of Things (IoT) covers objects and devices used by a user that are connected to the internet. Connected Devices have the ability to collect sensitive information on users and their daily activity [37]. While the Internet of Things enhances human comfort and convenience, it has raised questions amongst academics about security and privacy.
Internet of Things & Security
Researchers have uncovered that since Internet of Things technology was not designed with security in mind, as it was designed to provide novel features while minimizing device cost and size, the devices have limited hardware resources. This means that security tools cannot be installed in internet of Things devices, which makes it an easy target for cyber crimes. There are 3 typical ways that an agent can threaten IoT systems: 1. stealing information (ie.user credentials) 2. tracking user information (ie. location) and 3. taking control of a system (ie. through malware) [38]. A single Internet of Things device can compromise other connected devices, leading the collection of compromised devices to be used to attack computing assets and services. This means that criminals can leverage the power of Internet of Things technology can be used to hack connected devices, such as pacemakers, and cause potential physical harm to others [39]. Considering that the Apple Watch is an internet of Things device, data security, is a topic of rising concern with the product as compromised devices can affect other devices within the internet of Things.
At the same time, Internet of Things devices can be useful in criminal activities, by providing law enforcement with rich information. The interconnected nature of the devices means that experts are able to collect more data about criminals, if they are using a connected device [40]. While the data collected on users through the Apple Watch raises data privacy and security concerns, scholars point out that the product can be valuable in crime related investigations.
Increasing Disparities
The Apple Watch may indirectly contribute to the perpetuation inequality amongst minority populations. Since smartwatches are notably expensive products, the purchase of this technology is not accessible to every socioeconomic and demographic population. The majority of smartwatches are bought by young people with higher socioeconomic status [41]. Access to healthcare is lower for low-income populations, leading the inaccessibility of lower populations to gain access to health data through an Apple Watch to lead to further discrimination against people who cannot afford the watches [42]. Further, scholars have uncovered that the accuracy of algorithms for detecting certain health related conditions through the Apple Watch is not representative. Namely, the participants of the Apple heart study were on average 41 years old and 68% were white [43]. Therefore, the algorithms were not evaluated for a diverse group of users, causing there to be a lack of algorithmic accuracy for these populations.
Given the rising concerns about the disparities that Apple indirectly widens through its products, Apple has increasingly made commitments to diversity, equity, and inclusion. Specifically, Apple highlights that the number of employees from underrepresented communities (URCs) has increased by 64%, or over 18,000 people, and makes up nearly 50% of Apple’s U.S. workforce [44].
See also
References
- ↑ "Apple Watch Documentation." <https://www.att.com/buy/wearables/apple-watch-series-7-41mm-starlight-aluminum-starlight-sport.html?source=EC1NSpDES0000000P&tfn=wireless&WT.srch=1&wtExtndSource=PRODUCT_GROUP&gclsrc=aw.ds&&gclid=Cj0KCQiAjJOQBhCkARIsAEKMtO04UBmqiHJg_8MSWh-dvlXea5u8BGIgdlFT4PSreL3DnDeL_tfK11AaAs5REALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds>.
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/
- ↑ https://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Apple-Watch
- ↑ https://www.statista.com/chart/15035/worldwide-smartwatch-shipments/#:~:text=According%20to%20estimates%20from%20Counterpoint,leader%20in%20the%20smartwatch%20market.
- ↑ https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2020.615927/full
- ↑ https://appleinsider.com/inside/apple-watch
- ↑ https://www.wired.com/2015/04/the-apple-watch/
- ↑ https://www.wired.com/2015/04/the-apple-watch/
- ↑ https://www.wired.com/2015/04/the-apple-watch/
- ↑ https://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-3030492/Take-peek-inside-Apple-Watch-Infographic-reveals-firm-packs-components-needed-power-wearable.html
- ↑ https://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-3030492/Take-peek-inside-Apple-Watch-Infographic-reveals-firm-packs-components-needed-power-wearable.html
- ↑ https://www.iphonefaq.org/archives/974320
- ↑ https://www.commonsense.org/education/articles/privacy-and-security-evaluation-of-the-apple-watch
- ↑ https://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-3030492/Take-peek-inside-Apple-Watch-Infographic-reveals-firm-packs-components-needed-power-wearable.html
- ↑ https://www.lifewire.com/what-is-watchos-4690550
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/watchos/watchos-8/
- ↑ https://learning-oreilly-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/library/view/apple-watch-for/9781119558637/c05.xhtml#h2-3
- ↑ https://learning-oreilly-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/library/view/apple-watch-for/9781119658665/c08.xhtml#h2-6
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/shop/buy-watch/apple-watch
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/watch/whats-new-apdb93ea3872/8.0/watchos/8.0
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/watch/compare/
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/watch/whats-new-apdb93ea3872/8.0/watchos/8.0
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/watch/whats-new-apdb93ea3872/8.0/watchos/8.0
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2016/09/apple-nike-launch-apple-watch-nike/
- ↑ https://learning-oreilly-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/library/view/apple-watch-for/9781119558637/c01.xhtml#h2-2
- ↑ https://repositorio.iscte-iul.pt/handle/10071/14630
- ↑ https://www.fitbit.com/global/us/products/smartwatches
- ↑ https://www.fitbit.com/global/us/about-us
- ↑ https://www.statista.com/chart/15035/worldwide-smartwatch-shipments/#:~:text=According%20to%20estimates%20from%20Counterpoint,leader%20in%20the%20smartwatch%20market
- ↑ https://timreview.ca/article/1067
- ↑ https://timreview.ca/article/1067
- ↑ https://timreview.ca/article/1067
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30916041/#:~:text=The%20principle%20of%20nonmaleficence%20requires,level%20of%20competence%20and%20training
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7843431/
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7843431/
- ↑ https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(19)30553-4/pdf
- ↑ https://www.commonsense.org/education/articles/privacy-and-security-evaluation-of-the-apple-watch
- ↑ https://web-s-ebscohost-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/ehost/detail/detail?vid=0&sid=cbf01992-81a8-48e6-af22-021502434a67%40redis&bdata=JnNpdGU9ZWhvc3QtbGl2ZSZzY29wZT1zaXRl#AN=153038918&db=a9h
- ↑ https://link-springer-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/content/pdf/10.1007%2F978-3-319-99277-8.pdf
- ↑ https://link-springer-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/content/pdf/10.1007%2F978-3-319-99277-8.pdf
- ↑ https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2020.615927/full
- ↑ https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1901183
- ↑ https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1901183
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/diversity/
[[Category:]] [[]]